IoT analytics involves using specialized tools and techniques to analyze the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices in order to extract meaningful insights and inform decision-making. It helps organizations to better understand their operations, identify patterns and trends, and optimize their systems and processes.
What is IoT analytics?
IoT (Internet of Things) analytics refers to the process of collecting, storing, and analyzing data generated by the Internet of Things (IoT) devices. IoT devices are connected to the internet and are able to collect and transmit data about their environment, usage, and other characteristics. This data can be used to improve the performance and efficiency of the device, as well as to gain insights into the behavior and characteristics of the device’s users.
IoT analytics often involves the use of specialized software and tools to process and analyze the data generated by IoT devices. This may include data visualization tools, machine learning algorithms, and other advanced analytics techniques. The goal of IoT analytics is to extract valuable insights and knowledge from the data generated by IoT devices and to use this information to make informed decisions and optimize the performance of the device and its related systems.
IoT analytics architecture
Effectively implementing IoT architecture will guarantee that you have access to useful insights from IoT analytics whenever you need them. Think about each of the following IoT architecture components.
- Data generation: Continuous data is produced by sensors, IoT devices, and smart gadgets.
- IoT message broker and MQTT protocol: The MQTT protocol and an IoT message broker are used by IoT devices to communicate since internet connectivity is frequently intermittent. In order to communicate with other services that subscribe to particular topics within the message broker in order to access device data, the message broker employs a publish and subscribe technique.
- A streaming service: To provide dependable ingestion and delivery to a staging table in the cloud data warehouse, real-time device data is ingested and buffered using a streaming service.
- Cloud object storage: Cloud object storage is used to stage batch data prior to ingestion when the application calls for it. For instance, minute-by-minute data might be kept in cloud object storage, while longer-term aggregated data might be kept in the cloud data warehouse.
- Streaming data support: Make sure your cloud data warehouse supports JSON and other semi-structured data types natively for simple device data ingestion.
- IoT rules engine: The business logic needed by the application is hosted by an IoT rules engine, which runs on data from the message broker and the cloud data warehouse. The rules engine communicates with the controls through messages.
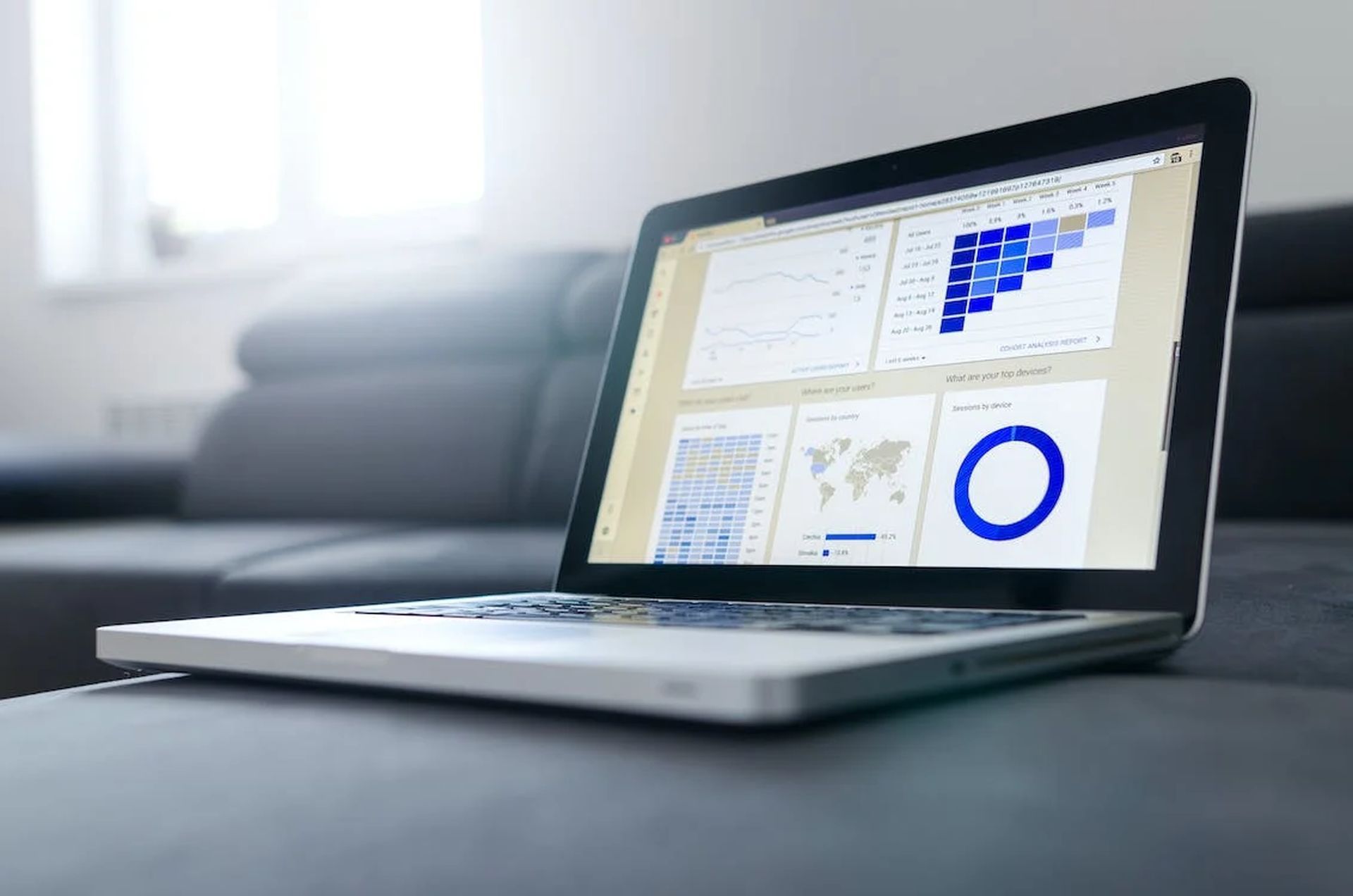

What are the types of IoT analytics?
There are several types of IoT analytics, including:
Descriptive analytics
Descriptive analytics involves summarizing and visualizing data to understand what has happened in the past. This type of analysis is useful for understanding trends and identifying patterns in the data.
Predictive analytics
Predictive analytics involves using data and machine learning algorithms to make predictions about future events. This type of analysis is useful for forecasting demand, identifying potential problems, and making informed decisions.
Prescriptive analytics
Prescriptive analytics involves using data and machine learning algorithms to not only predict what will happen in the future but also recommend actions to take in response. This type of analysis is useful for automating decision-making and optimizing processes.
Real-time analytics
Real-time analytics involves analyzing data as it is generated by IoT devices in order to make immediate decisions or take immediate actions. This type of analysis is useful for detecting and responding to problems in real time.
Historical analytics
Historical analytics involves analyzing data over a longer period of time, typically months or years. This type of analysis is useful for understanding long-term trends and identifying patterns that may not be immediately apparent in real-time data.
How does IoT analytics work?
IoT analytics typically involves several key steps. Let’s review them step by step.
Data collection
The first step in IoT analytics is to collect data from IoT devices. This may involve installing sensors or other data collection devices on the device or connecting the device to a network that allows it to transmit data.
Data storage
Once the data has been collected, it needs to be stored in a central repository or database. This may be done using a cloud-based storage solution or by using on-premises servers or storage devices.
NB-IoT will shape the future of smart cities
Data processing
Once the data has been collected and stored, it needs to be processed and analyzed. This may involve using specialized software and tools to filter, clean, and transform the data, as well as to extract insights and generate reports.
Data visualization
To make the insights and analysis generated by IoT analytics more easily understood, it is often helpful to use data visualization techniques such as charts, graphs, and maps. These can help to highlight trends, patterns, and relationships in the data that may not be immediately apparent from raw data alone.
Data-driven decision making
The final step in IoT analytics is to use the insights and analysis generated from the data to inform decision-making. This may involve adjusting the performance or behavior of the IoT device or making changes to related systems and processes to optimize their performance and efficiency.
Overall, the goal of IoT analytics is to extract valuable insights and knowledge from the data generated by IoT devices and to use this information to improve the performance and efficiency of the device and its related systems. By analyzing data from IoT devices, organizations can gain a deeper understanding of how the device is being used, identify opportunities for optimization, and make informed decisions that drive business value.

The use cases of IoT analytics
There are many different business use cases for IoT analytics, depending on the specific industry and needs of the organization. Some common examples include:
- Supply chain optimization: IoT devices can be used to track the movement and status of goods throughout the supply chain, allowing organizations to optimize logistics and improve efficiency.
- Predictive maintenance: By analyzing data from IoT sensors on equipment and machines, organizations can identify potential problems before they occur, allowing for proactive maintenance and reducing the risk of equipment failure.
- Customer experience: IoT analytics can be used to track customer interactions with products and services, allowing organizations to identify opportunities to improve the customer experience and increase customer satisfaction.
- Asset tracking: IoT devices can be used to track the location and status of assets, such as vehicles or equipment, allowing organizations to optimize the use of these assets and reduce the risk of loss or theft.
- Environmental monitoring: IoT sensors can be used to monitor environmental conditions, such as temperature, humidity, and air quality, allowing organizations to optimize energy usage and improve sustainability.
IoT analytics jobs and opportunities
There are a variety of job roles related to IoT analytics, including:
- Data scientist: Data scientists are responsible for designing and implementing algorithms and models to analyze and interpret IoT data. They may use techniques such as machine learning and statistical analysis to extract insights and identify patterns in the data.
- IoT data engineer: IoT data engineers are responsible for designing and building the infrastructure and pipelines necessary to collect, store, and process IoT data. This may involve working with databases, cloud platforms, and data processing tools to ensure that data is available for analysis in a timely and reliable manner.
- IoT solution architect: IoT solution architects are responsible for designing and implementing end-to-end IoT solutions. They may work closely with data scientists and data engineers to ensure that the necessary data is collected, processed, and analyzed to meet the needs of the business.
- BI analyst: Business intelligence analysts are responsible for using data to inform business decisions. They may work with IoT data to understand trends, identify opportunities, and make recommendations to stakeholders.
- IoT project manager: IoT project managers are responsible for planning and executing IoT projects. They may work closely with cross-functional teams to ensure that projects are delivered on time and within budget.
IoT sensors smarten everyday objects with awareness and cognition
Best IoT analytics companies and platforms
There are many different companies and platforms that offer IoT analytics solutions, and it can be difficult to determine which one is the best fit for a particular organization. Some of the top IoT analytics companies and platforms include:
AWS IoT Analytics
AWS IoT Analytics is a fully-managed service that makes it simple to run complicated analytics on enormous volumes of IoT data without worrying about the expense and complexity involved in developing your own IoT analytics platform.
SensorCloud
The SensorCloud platform from MicroStrain is a cutting-edge platform for storing, visualizing, and remotely managing sensor data. It makes use of strong cloud computing technologies to offer exceptional data scalability, quick visualization, and user-programmable analysis.

Exosite ExoSense IoT
ExoSense is a remote condition monitoring tool that may give operational insight into industrial assets, systems, and equipment. It can be set up in a matter of minutes. Any firm may now gather and visualize sensor data to give new features and services to consumers, estimate maintenance needs, and warn users of dangerous operating situations.
TrendMiner
Industrial Analytics Solutions for Process Manufacturing with Self-Service Self-service data analytics are provided by TrendMiner, a Software AG firm that is a part of the IoT & Analytics division, to optimize process performance in sectors like chemical, petrochemical, oil & gas, pharmaceutical, metals & mining, and other process manufacturing industries. With the help of no data scientists, consumers can directly query time-series data using the high-performance analytics engine at the foundation of TrendMiner software.
Google Cloud IoT Core
In order to connect, monitor, and consume data from widely scattered devices in an easy and safe manner, Google has developed a completely managed service.
Conclusion
From a business perspective, IoT analytics can offer significant risks, rewards, and benefits. Some potential risks include data security and privacy concerns, as well as the risk of investing in technologies that may become obsolete or unsupported.
However, the rewards of IoT analytics can also be significant. By collecting and analyzing data from IoT devices and systems, businesses can gain insights into their operations, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions. This can lead to cost savings, increased productivity, and competitive advantage.
Additionally, the benefits of IoT analytics extend beyond the business itself, as the insights gained through analysis can be used to improve products and services and to solve problems in a variety of industries and sectors. Overall, while there are risks associated with IoT analytics, the potential rewards and benefits make it a valuable tool for businesses looking to improve their operations and drive growth.





