In 1959, Arthur Samuel defined machine learning as a “Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed”. It’s a science of algorithms and automation; the algorithms “learn” from the dataset, identifying patterns or classifying trends for instance, and then automates output- whether that’s sorting data into categories or making predictions on future outputs. In this edition of “Understanding Big Data“, we’ll be taking a more in-depth look at the term and its many different forms and applications.
When many people hear the term “machine learning”, they conjure up mental images of robots who walk, climb or clean houses. In reality, machine learning starts alot closer to home. When you open your emails, spam has been filtered out from your important messages by an algorithm that has learnt to classify “spam” and “not spam”. Your Facebook news feed features posts from your closest friends because an algorithm has examined your likes, tags and photos to decipher who you connect with most. When you upload a photo and the website identifies your face, it’s fuelled by a facial recognition algorithm. When you use a search engine, you see the best and most relevant content first because of a sophisticated search ranking algorithm. In short, machine learning permeates our lives.
Often, people use the terms “machine learning” and “data mining” interchangably, and this is inexact; there is a distinction. Machine learning is centred around making predictions, based on already-identified trends and properties in the training data set. Data mining is the process of discovering of unidentified patterns and properties in the data, as part of the discovery stage of data analysis. The two do intersect; machine learning techniques are often incorporated into data mining, and unsupervised machine learning follows the same principles as data mining.
Some of the main categories of machine learning include:
- Supervised Learning- In supervised learning, algorithms are trained on labelled examples (in spam filters, for instance, algorithms are trained by inputting emails with the output “Spam” and “Not spam”). It then generalises the function between inputs and outputs, and eventually learns to speculate outputs itself (e.g., tell the difference between spam and important mail). Spam filters are an example of a classification problem; another major problem within supervised learning is regression, which models and analyses the relationship between variables. Some applications of supervised learning include handwriting recognition and speech recognition (mostly using Hidden Markov Models). In a recent Google Hangout, Stanford Professor and Coursera Co-Founder Andrew Ng identified speech recognition as one of the most exciting fields for the future of machine learning; he envisioned a future in which we have phones with reply and delete buttons, and everything else will be speech-automated.
Google’s neural network’s understanding of a cat; source
- Unsupervised Learning- The input data in machine learning isn’t labelled and the output isn’t known. The aim of unsupervised learning is find the hidden structures within the data. One main class of problem associated with unsupervised learning is Clustering, which uses the inherent structures of data to group data points together by common properties. An application of this is Amazon book recommendations, which cluster together users with similar buying habits and tastes. Another example of unsupervised learning is Google’s neural network; it was fed 10,000 Youtube thumbnails and without being told what to look for, began to categorise and group the images of together. Due to the obscene amount of cat videos on Youtube, the network eventually came up with a single image of what it understood to be a cat, which you can see above.
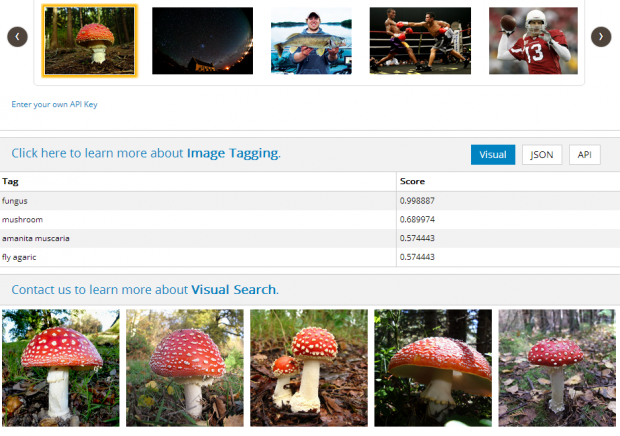
AlchemyAPI’s Alchemy Vision software; source
- Deep Learning- Deep learning involves teaching computers how to think hierarchically and model high-level abstractions. Deep learning breaks down the data into different characteristics on different levels (i.e in image classification, one level might be pixels, the next might be edges)- the algorithms learn what the relationships between these characteristics are on different levels to understand the data input. One example of deep learning is AlchemyAPI‘s computer vision system, which can understand and classify over 10,000 concepts in images, and identify multiple concepts in one image. Try the demo out for yourself here.
- Reinforcement Learning- In reinforcement learning, the system is not told which actions to take, but discovers which actions work best based on what “rewards” it yields from them. Reinforcement learning is used frequently in robotics; a list of applications of reinforcement learning can be found here, arguably the coolest of which is this autonomous helicopter, created by Andrew Ng et al.
So machine learning extends vastly beyond the obvious remit of robotics- it’s a part of our everyday lives, operating behind the scenes when we open our emails, give commands to Siri, search for book recommendations or search for images. It’s not just a part of our lives; it’s making our lives easier.
(Image credit: Flickr)
Eileen McNulty-Holmes – Editor
Eileen has five years’ experience in journalism and editing for a range of online publications. She has a degree in English Literature from the University of Exeter, and is particularly interested in big data’s application in humanities. She is a native of Shropshire, United Kingdom.
Email: eileen@dataconomy.com
Interested in more content like this? Sign up to our newsletter, and you wont miss a thing!
[mc4wp_form]