A research team led by Professor WANG Mingtai at the Hefei Institutes of Physical Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has developed a refined method for growing titanium dioxide nanorod arrays (TiO₂-NA) with controllable spacing, maintaining constant individual rod size, and demonstrated its utility in high-performance solar cells.
The findings, published in the journal Small Methods, introduce a method for crafting nanostructures applicable across clean energy and optoelectronics. Single-crystalline TiO₂ nanorods are effective for light harvesting and charge conduction, making them suitable for solar cell, photocatalyst, and sensor applications. Conventional fabrication techniques for these nanorods typically link rod density, diameter, and length, meaning adjustments to one parameter affect the others, frequently impacting device efficiency.
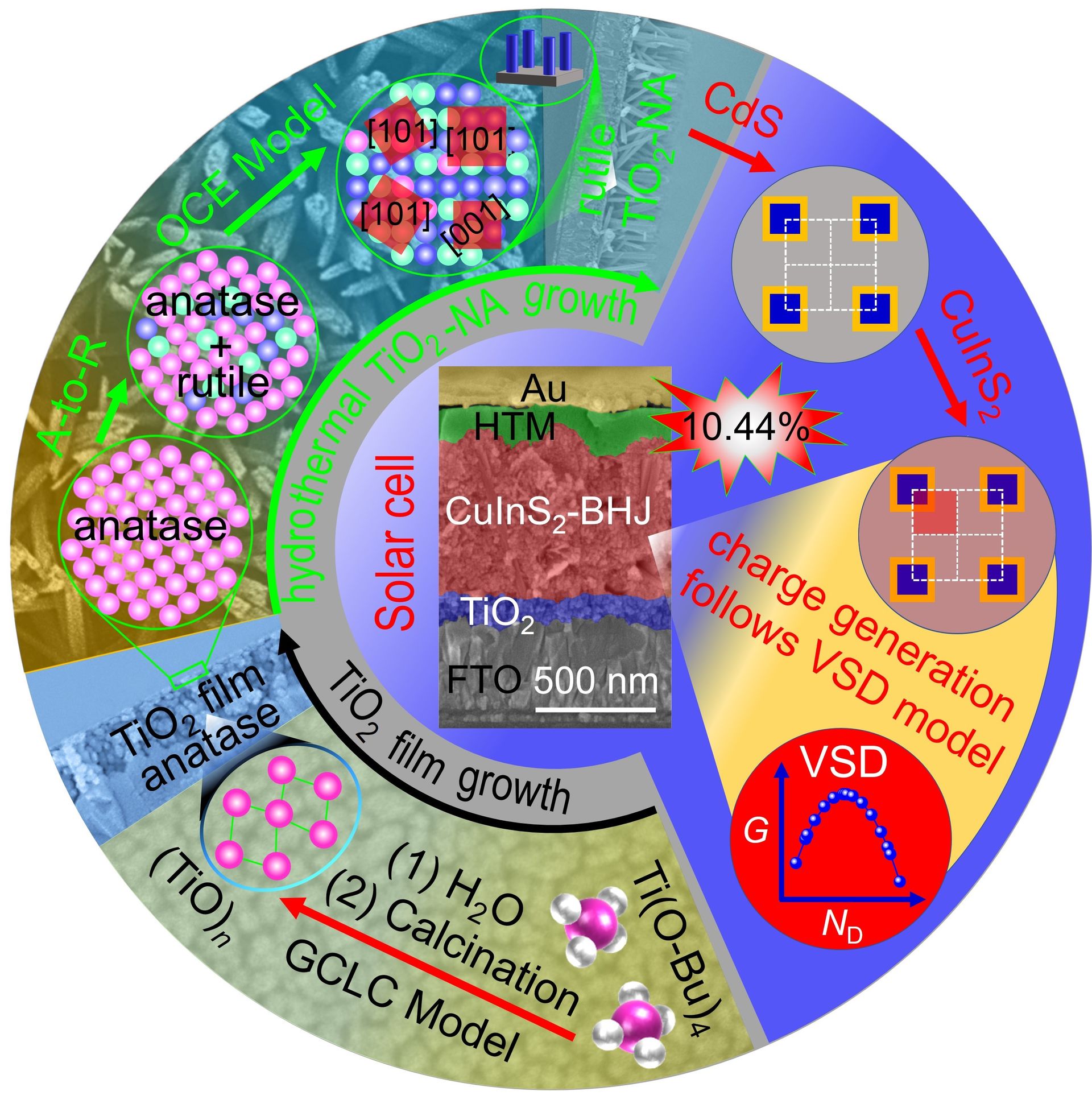
The research team addressed this limitation by extending the hydrolysis stage of a precursor film. This extension led to the assembly of longer “gel chains,” which in turn formed smaller anatase nanoparticles. When this anatase film underwent hydrothermal treatment, these nanoparticles converted in situ into rutile ones, functioning as seeds for subsequent nanorod growth. This controlled hydrolysis stage provides a mechanism to regulate rod density without altering the dimensions of the individual nanorods.
This AI lab wants to automate scientific discovery
Using this approach, the team successfully produced TiO₂-NA films where the rod diameter and height remained consistent while the number of rods per unit area varied. When these films were integrated into low-temperature-processed CuInS₂ solar cells, they achieved power conversion efficiencies exceeding ten percent, reaching a peak efficiency of 10.44 percent. To explain the impact of spacing on performance, the team introduced a Volume-Surface-Density (VSD) model. This model elucidates how variations in rod density influence light trapping, charge separation, and carrier collection within the solar cell structure.
This research addresses previous limitations in regulating nanostructures by establishing a comprehensive system that links macro-process regulation with microstructure evolution and device performance optimization.





