Ever wondered how robots could ace navigation like seasoned pros? Google’s Gemini AI experiment dives into this with style and smarts!
Google’s Gemini AI experiment focused on equipping robots with enhanced navigational abilities using the Gemini 1.5 Pro system. This system is distinguished by its capability to process a vast amount of contextual information—up to 1 million tokens—allowing robots to effectively interpret and utilize human instructions, video tours, and various multimodal inputs for navigation.
The Gemini 1.5 Pro system’s most critical feature is its ability to handle a vast context length, which enables robots to retain and utilize detailed spatial information over extended periods. This capability is crucial for navigating complex and dynamic environments without traditional mapping solutions.
How can Gemini 1.5 Pro’s long context window help robots navigate the world? 🤖
A thread of our latest experiments. 🧵 pic.twitter.com/ZRQqQDEw98
— Google DeepMind (@GoogleDeepMind) July 11, 2024
During the experiment, robots received instructions through multiple sensory channels:
- Human instructions: Clear verbal commands and descriptive cues that guide robots to specific locations within a designated space.
- Video tours: Visual representations of the environment, which help robots create a mental map and understand spatial relationships.
- Map sketches and audio references: Additional cues provided through map sketches on whiteboards, audio instructions referencing key locations, and visual markers like toys or boxes strategically placed within the environment.
The experiment was conducted in a real-world operational area spanning over 9000 square feet. Within this space, robots were tasked with performing a diverse range of 57 specific tasks. These tasks encompassed various actions and operations that required the robots to navigate autonomously and efficiently based on the inputs provided.
We took the robots on a tour of specific areas in a real-world setting, highlighting key places to recall – such as "Lewis’s desk" or "temporary desk area". Then, they were asked to lead us to these locations. 🏢
Watch more. ↓ pic.twitter.com/Sptm6q31CL
— Google DeepMind (@GoogleDeepMind) July 11, 2024
Performance and success rate of Gemini-powered robots
According to Google’s findings, the Gemini-enabled robots achieved an impressive success rate of 90% across the 57 tasks assigned. This high success rate underscores the effectiveness of the Gemini 1.5 Pro system in enhancing robot autonomy and operational efficiency in complex environments.
Behind the scenes, the Gemini AI system processes the multimodal inputs received from the environment. It creates topological graphs—a simplified representation of spatial connectivity based on video frames and contextual instructions. These graphs serve as navigational maps that guide robots in real-time, enabling them to navigate without the need for continuous external mapping updates.
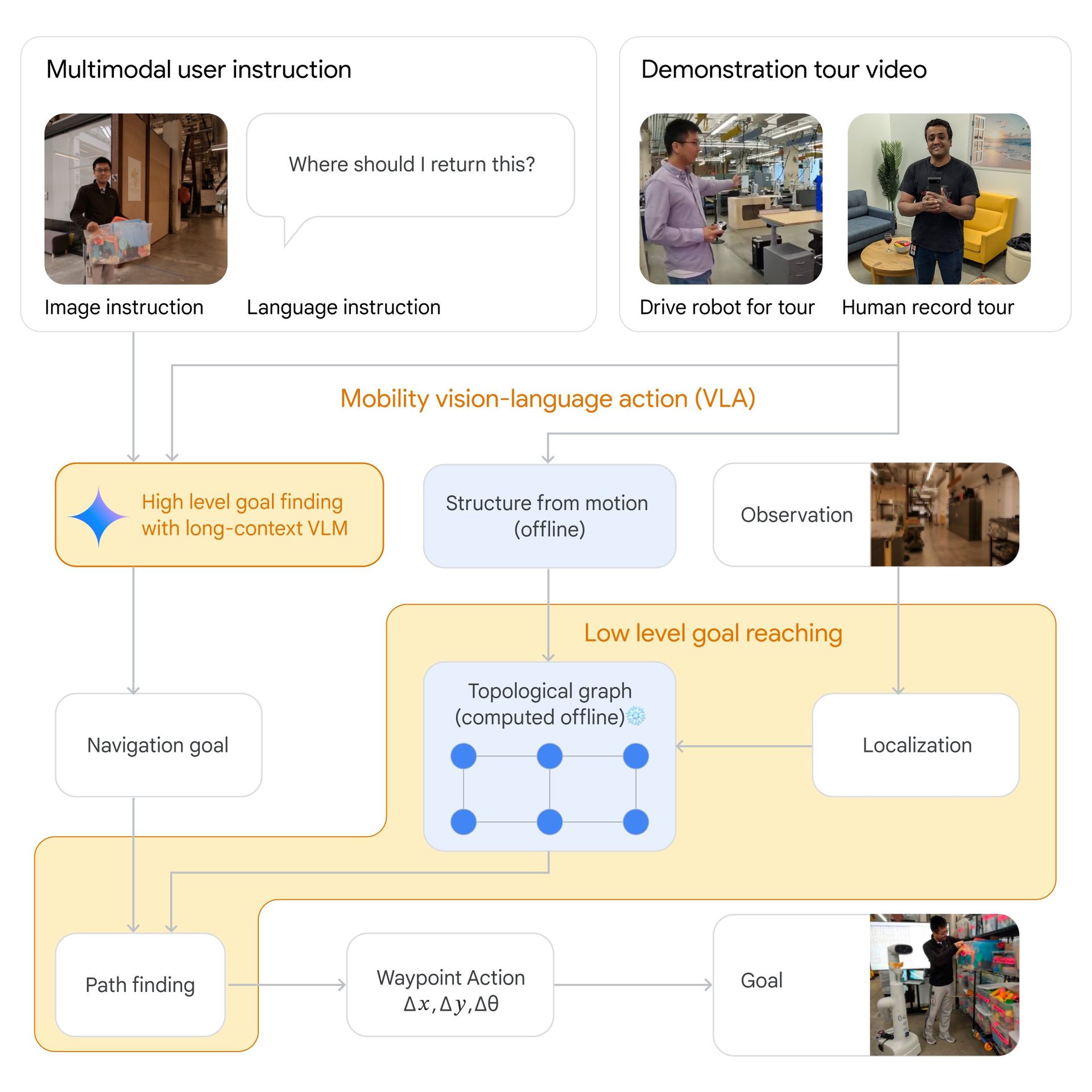
Need a recap? Google uses Gemini AI to train its robots for improved navigation and task completion. Robots can process extensive information with Gemini 1.5 Pro’s extended context window, enabling them to respond to natural language instructions more effectively. By filming video tours of environments like homes or offices, researchers teach robots to understand their surroundings. The robots, equipped with Gemini, achieved a 90% success rate across 50+ tasks in a 9,000+ square-foot area. Gemini also helps robots plan actions beyond navigation, such as fetching food from the fridge. While there are still processing delays of 10–30 seconds per instruction, Google aims to advance these capabilities further in future research.
Featured image credit: Google DeepMind/X





