Researchers in China and the US have revealed a novel fingerprint hack named PrintListener capable of stealing your fingerprint data, not from photos or lifted prints, but from the faint sound your finger makes when swiping your smartphone screen.
Fingerprint authentication has become synonymous with security on our smartphones and devices. Worth an estimated $100 billion by 2032, the market reflects our deep trust in biometric protection.
But PrintListener demonstrates that, like any technology, biometrics have vulnerabilities.
How PrintListener works?
Our everyday apps, like Discord, Skype, FaceTime, and many others, were designed for communication. But what if they could do more than transmit your voice?
Researchers behind PrintListener raise a disturbing possibility: These apps could be acting as an unwitting accomplice to a fingerprint hack. Every time you swipe across your smartphone screen, even during those seemingly casual conversations, your microphone might be inadvertently recording a hidden soundtrack: The subtle friction generated by your fingerprint ridges.
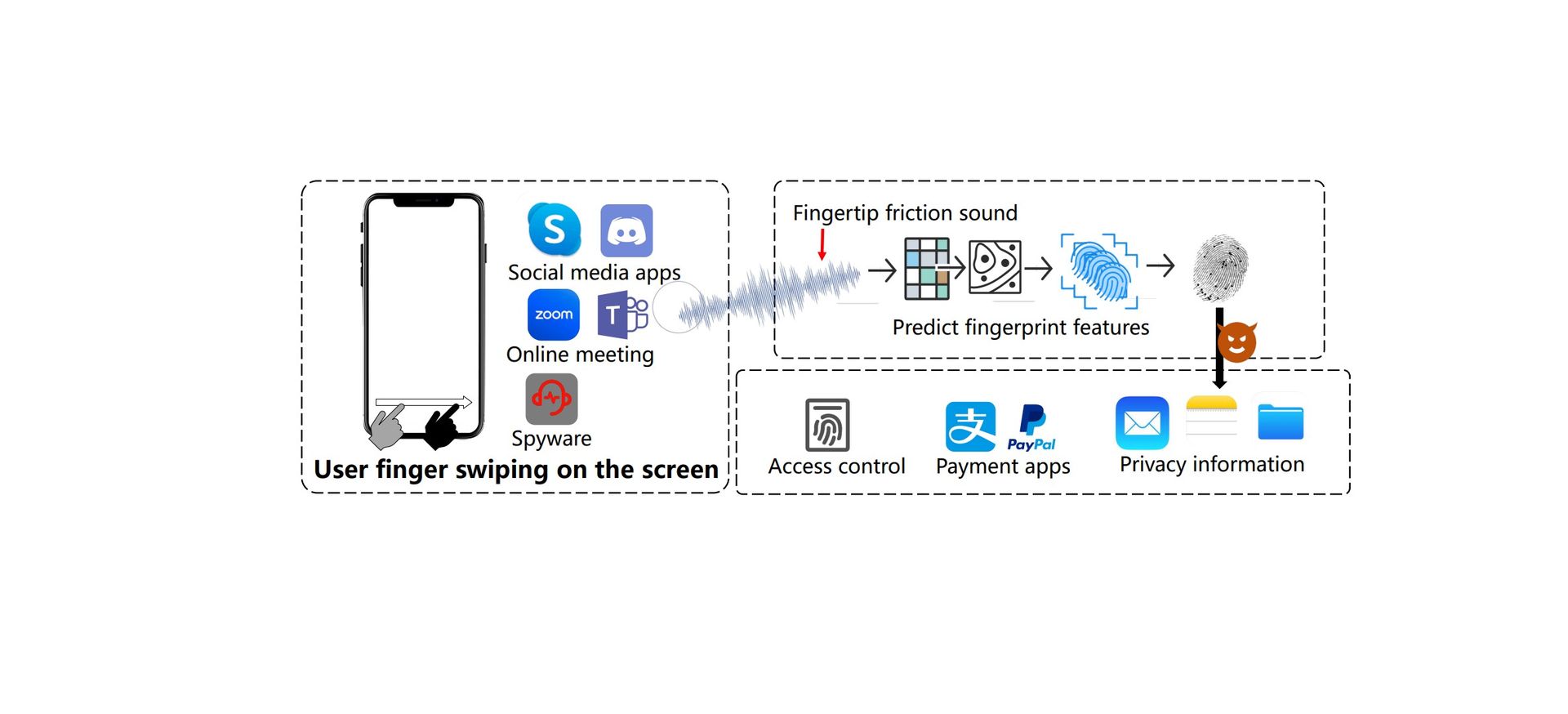
Turning sounds into fingerprint data
PrintListener isn’t just about hearing these micro-sounds; it’s about interpreting them. The tool employs sophisticated analysis to dissect the faint acoustics of your swipes, meticulously searching for patterns unique to your fingerprint.
Unlike traditional dictionary attacks, which rely on pre-built databases of common fingerprint patterns, PrintListener can use this newly captured audio data to enhance attacks like MasterPrint. That means potentially customizing fingerprint forgeries with far greater accuracy.
Fingerprint hack has a shocking success rate
The effectiveness of PrintListener lies in its numbers. Researchers boast a worrisome success rate. Within just five attempts, PrintListener could crack 27.9% of partial fingerprints. Even more chilling, 9.3% of the time, PrintListener was able to reconstruct complete fingerprints from swiping sounds alone.
It highlights how this novel exploit transforms harmless interactions with seemingly unassuming apps into a potent tool for hackers.
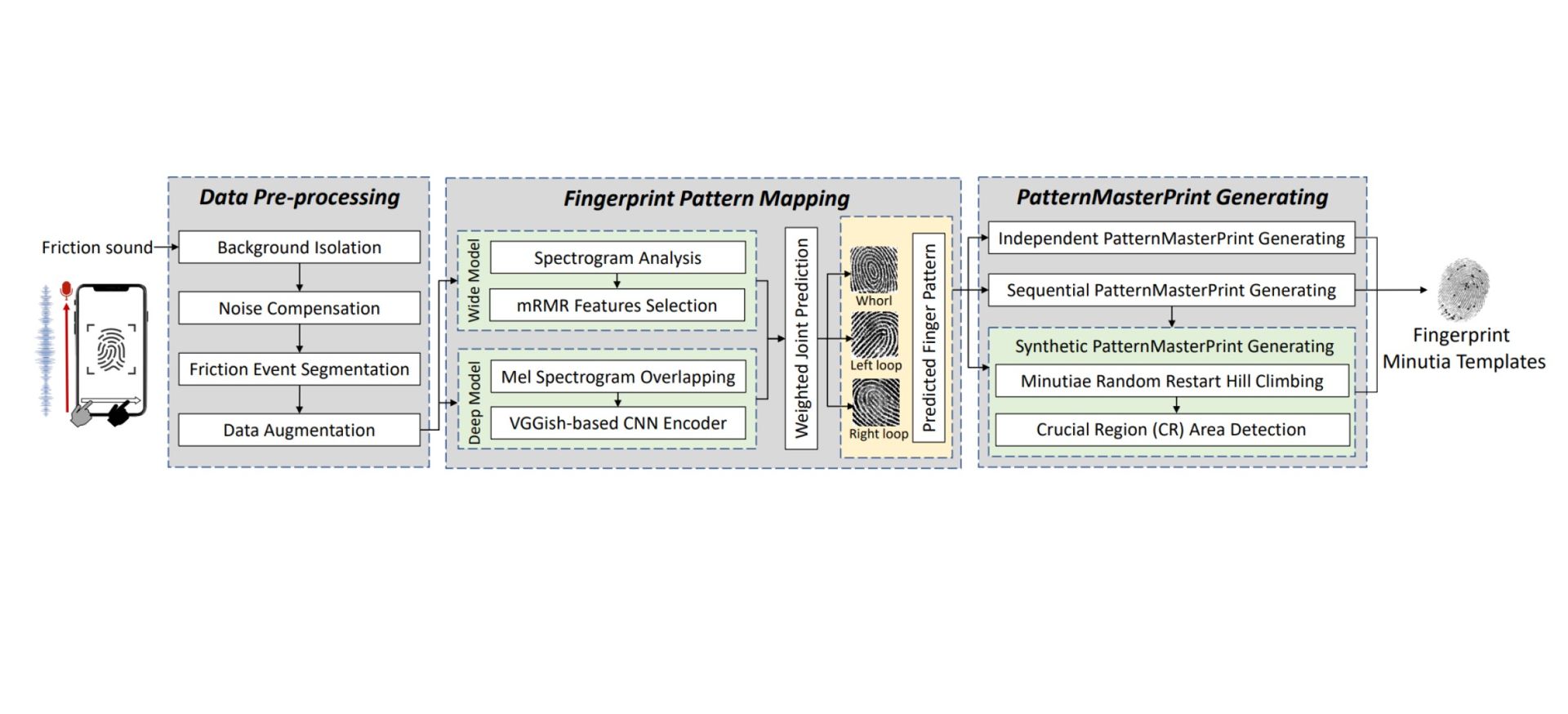
Cyberthreats are constantly evolving
The PrintListener revelation underscores a broader trend in cybersecurity: There is a new sophisticated hacking method being developed day by day. Technology intertwines with almost every aspect of our lives nowadays and hackers are constantly searching for and discovering new vulnerabilities, often in the most unexpected places.
From AI-powered phishing attacks that mimic trusted voices to malware embedded within seemingly innocuous QR codes, the tactics of cybercriminals evolve at an alarming pace.
Let’s consider a few recent examples:
- WhisperGate: In early 2022, this destructive malware emerged, masquerading as legitimate ransomware while quietly wiping entire systems of Ukrainian organizations in a politically motivated attack
- Log4j vulnerability: Late 2021 saw the revelation of a critical zero-day vulnerability in a widely used logging library. Log4j‘s extensive presence meant a scramble ensued, exposing numerous systems to remote control exploits
- Supply chain attacks: Hackers aren’t just breaking in; they’re infiltrating systems from within. Through vulnerabilities in the software development ecosystems (like the infamous SolarWinds hack), attackers manage to compromise widely used products and services, leading to massive downstream impacts
These examples underscore that traditional approaches to security won’t cut it. Our technology isn’t just expanding, it’s becoming more complex and interdependent. Hackers relentlessly hunt for weaknesses in these complex systems, exploiting both technological flaws and the often-overlooked human element.
Protecting yourself against emerging threats
The PrintListener attack and other emerging cyber threats might feel daunting, but remember you have the power to protect yourself. Embrace proactive security measures that drastically reduce your risk.
Here’s a breakdown of essential actions you can take:
- Control your apps: Conduct an audit of your apps. Check which ones have microphone and camera access and disable it for those who don’t genuinely need these permissions for their core functionality
- Biometrics: Use with Caution: Biometric security features like fingerprint and facial recognition offer convenience, but don’t treat them as foolproof. View them as useful tools rather than unbreakable shields
- Passwords are paramount: Choose complex, unique passwords for every account, and never reuse them. Wherever possible, turn on multi-factor authentication (MFA), which requires an additional code or confirmation alongside your password
- Fight phishing: Be skeptical of unexpected emails, texts, or social media messages, even if appearing to come from familiar sources. Verify a sender’s identity before opening any links or attachments
- Updates matter: Ensure you have the latest security updates for your operating system and apps. These frequent patch vulnerabilities, minimize the openings hackers could exploit
By implementing these basic yet powerful security practices, you’ll greatly enhance your digital protection against the constantly evolving cyber threats.
Featured image credit: George Prentzas/Unsplash.





