Tesla is preparing for a convergence of automotive and space technology. According to a recent patent filing published on December 4, 2025, the electric vehicle giant is exploring ways to integrate satellite antennas—likely for SpaceX’s Starlink—directly into the roofs of its cars. The patent, titled “Vehicle Roof Assembly with Radio Frequency Transparent Material,” outlines a method to hide satellite receivers within the car’s structure without compromising aesthetics or aerodynamics.
Metal and glass block signals are a problem for the Tesla Starlink antennas
Tesla vehicles are already among the most connected machines on the planet, relying heavily on cellular networks for features ranging from Autopilot data collection to over-the-air software updates. However, cellular coverage has its limits, especially in rural areas.
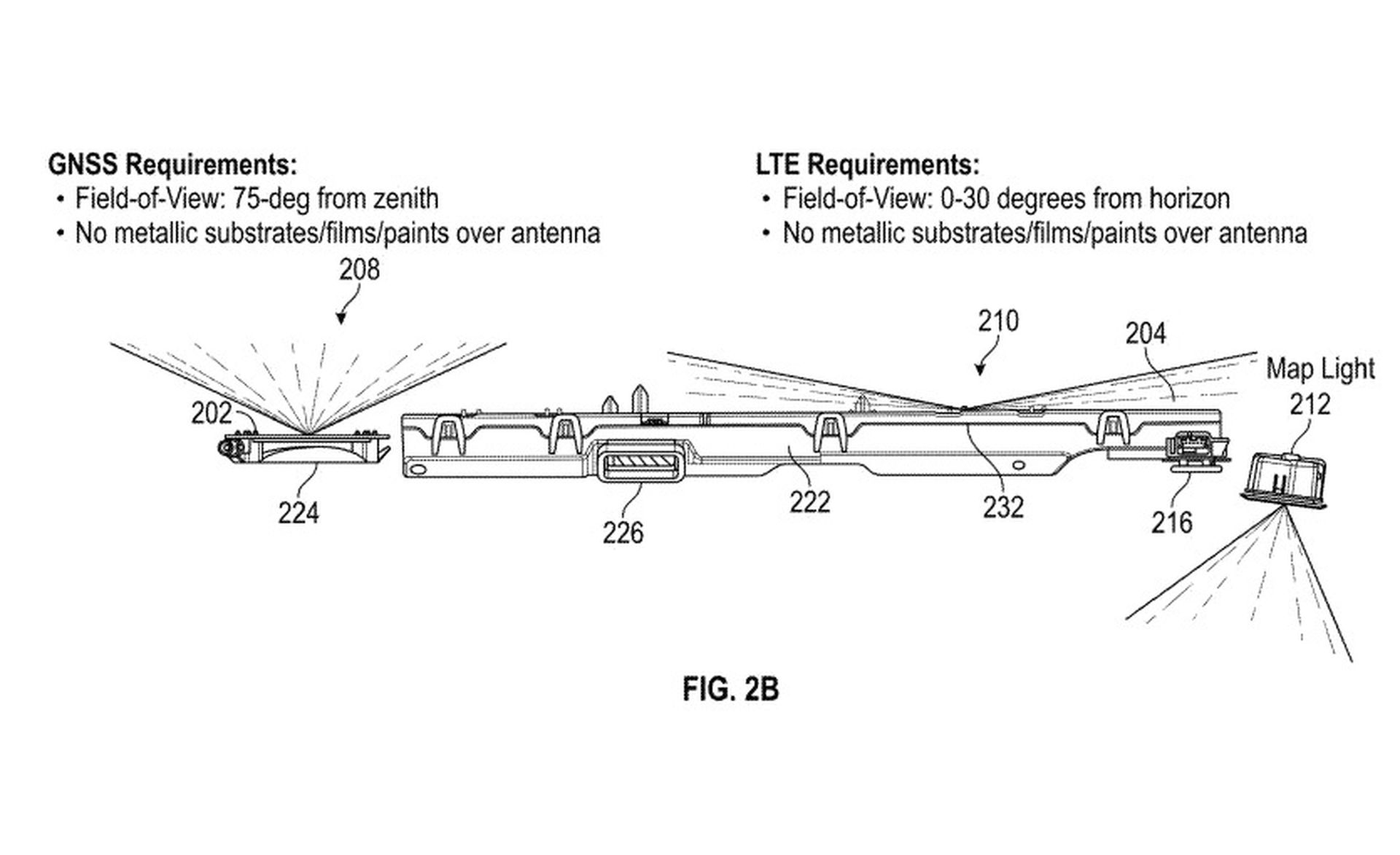
The patent filing notes a specific engineering challenge: traditional vehicle roofs made of metal or standard glass often block or weaken satellite signals. This makes it difficult to conceal an antenna inside the cabin. To solve this, Tesla proposes using a “radio frequency transparent” construction.
A high-tech hidden antenna is the solution
Tesla’s solution involves a multi-layered roof design that utilizes specific polymer blends, such as Polycarbonate (PC) and Acrylonitrile Styrene Acrylate (ASA). These materials provide a robust structural integrity similar to standard car roofs but allow radio frequencies to pass through unimpeded.
By using these materials, Tesla can integrate antennas directly into the roof structure. This means the car could maintain communication with satellites and external devices without requiring a visible, external dish that would ruin the car’s aerodynamics or design.
Starlink integration and always-on connectivity
While the patent document does not explicitly name “Starlink,” the implication is clear. Integrating SpaceX’s high-bandwidth, low-latency satellite internet would offer Tesla drivers distinct advantages:
- Seamless connectivity: Vehicles could switch smoothly between 5G cellular networks and the Starlink satellite network, ensuring the car remains online even in dead zones or during natural disasters.
- Enhanced autonomy: Continuous connectivity is vital for the future of autonomous driving systems and Tesla’s planned Robotaxi network, which requires constant data streams for real-time traffic and mapping updates.
- Entertainment: High-speed satellite internet would support high-definition video streaming and online gaming for passengers, regardless of location.
This move aligns with broader developments at SpaceX. Recent trademark filings have revealed the company’s intent to use the name “STARLINK MOBILE” for services involving the “two-way real-time transmission” of voice, video, and data via wireless devices. SpaceX has already signed deals with carriers like T-Mobile US and Ukrainian telecom giant Kyivstar to offer direct-to-cell technology.
For Tesla, this technology could provide a competitive edge at a time when the company faces market challenges, including sales fluctuations and regulatory scrutiny in California regarding its Full Self-Driving marketing. By effectively turning its cars into mobile satellite nodes, Tesla continues to leverage Elon Musk’s cross-company synergy to push EV technology forward.