You might have an iPhone 13, iPhone 14, or even the classic third‑generation iPhone SE that’s been with you through thick and thin. These models have proven their worth over time with a familiar design, reliable build, and a user experience that feels like home.
Then there’s the fresh face on the block—the iPhone 16e. It promises cutting‑edge performance, modern features, and a price that challenges what you’d expect from a new Apple device. It’s a leap forward that seems to offer the best of both worlds: the reliability you know and the innovations you crave without the hefty price tag.
iPhone 16e vs. iPhone SE 3 vs. iPhone 14 vs. iPhone 13
Our conversation today will dive into four key models: the trusted iPhone 13, the refined iPhone 14, the ever‑practical iPhone SE (3rd Gen), and the exciting new iPhone 16e. We’re here to help you figure out if upgrading or switching makes sense for you.

Display technology & experience
- Size differences:
The iPhone 13, iPhone 14, and iPhone 16e all sport a 6.1‑inch display, which has become the standard size for many users seeking a good balance between screen real estate and one‑handed usability. In contrast, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) features a much smaller 4.7‑inch screen. This difference in size is more than just a number—it affects everything from media consumption and gaming to simple tasks like texting and web browsing. While the SE’s compact dimensions appeal to those who favor a nostalgic, pocket‑friendly design, the larger screens on the other models provide a more immersive viewing experience. - Screen quality – OLED vs. LCD:
The iPhone 13, 14, and 16e all use OLED technology for their displays. OLED panels are renowned for their deep blacks, vibrant colors, and excellent contrast ratios (typically around 460 ppi), making them ideal for HDR content and cinematic experiences. On the other hand, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) retains a Retina HD display that uses LCD technology, which, while still very capable, does not match the contrast or power efficiency of OLED. The choice between OLED and LCD can be a deciding factor for users who prioritize display quality and energy efficiency. - Resolution and brightness comparisons:
In terms of pixel density and overall sharpness, the OLED displays on the iPhone 13, 14, and 16e deliver roughly 460 ppi. This ensures that images and text appear crisp and detailed even at close range. The iPhone SE’s LCD, however, has a resolution that yields approximately 326 ppi, which may be noticeable to users accustomed to the finer detail of modern OLED screens. Additionally, brightness levels on OLED displays are typically higher and more consistent—enhancing outdoor readability—while the SE’s screen may struggle under direct sunlight. - Additional display features:
All the OLED models include advanced features such as HDR support, True Tone technology for natural color reproduction, and Haptic Touch for intuitive interactions. These enhancements ensure that users not only enjoy excellent visuals but also benefit from adaptive technologies that adjust the display’s appearance based on ambient light. Although the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) includes True Tone and Haptic Touch, it lacks the HDR capabilities of its OLED counterparts, which means that dynamic range and contrast in high‑quality video and photography might not be as impressive.
Why the iPhone 17 Pro Max could be a copy-paste of the iPhone 17 Pro
Processor & performance
- A15 Bionic in iPhone 13, 14, and SE (3rd Gen) vs. A18 in iPhone 16e:
The iPhone 13, iPhone 14, and iPhone SE (3rd Gen) are powered by the A15 Bionic chip—a highly capable processor that has set a strong benchmark since its introduction. This chip delivers robust performance through a 6‑core CPU (with a combination of performance and efficiency cores), a 4‑core or 5‑core GPU depending on the model, and a 16‑core Neural Engine for machine learning tasks. In contrast, the new iPhone 16e is equipped with the A18 chip, which not only offers a higher clock speed but also comes with architectural improvements that enhance energy efficiency and overall performance. This upgrade translates into faster processing, smoother multitasking, and better longevity when it comes to future iOS updates and app performance. - Impact on speed, energy efficiency, and future‑proofing:
The transition from the A15 to the A18 is significant for users who demand the latest performance benchmarks. The A18 chip’s increased processing power and improved energy management mean that everyday tasks—from gaming to video editing—will be more fluid and less likely to encounter lag. Moreover, a more efficient chipset often translates to better battery performance, ensuring that the device remains responsive and power‑efficient even under heavy usage. For future‑proofing, the A18’s advanced capabilities mean that users are less likely to feel left behind as software and app demands continue to rise. - GPU differences and real‑world performance implications:
The iPhone 13, 14, and SE (3rd Gen) benefit from a GPU configuration that is sufficient for most current mobile applications and gaming experiences. However, the slight differences—such as the extra GPU core in certain variants of the iPhone 13 and 14—can offer a marginal edge in graphics‑intensive tasks. The iPhone 16e’s A18 includes a dedicated 4‑core GPU that, although numerically similar to some A15 configurations, benefits from improved architecture and optimization. In real‑world usage, this means more fluid animations, better handling of high‑resolution graphics, and an overall smoother visual experience, especially when engaging with graphics‑heavy applications or games.
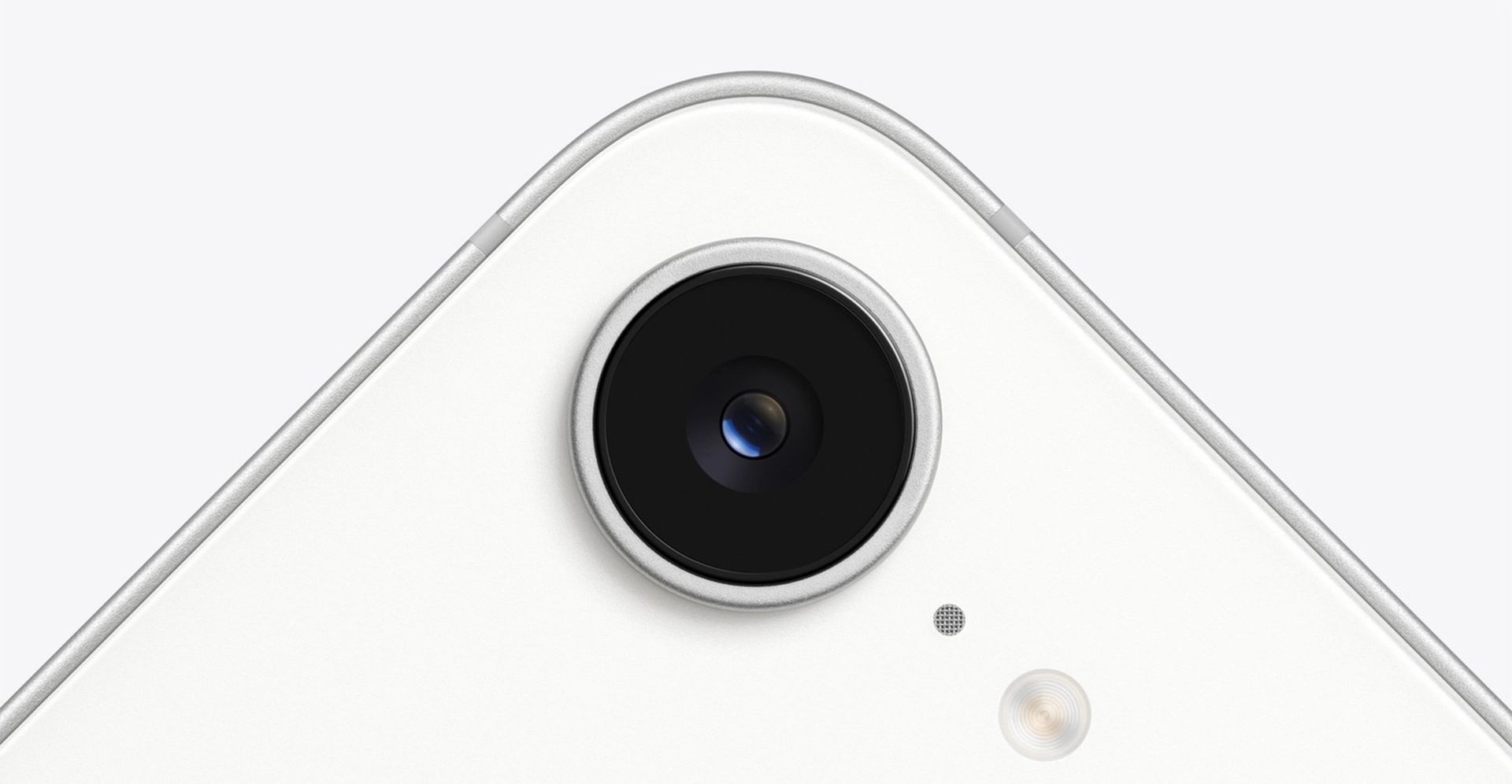

Camera systems
- Multi‑lens setups on iPhone 13 and iPhone 14 vs. single‑lens on iPhone SE (3rd Gen):
Both the iPhone 13 and iPhone 14 series feature multi‑lens camera systems that include a combination of wide and ultra‑wide lenses, offering versatility in capturing landscapes, portraits, and close‑up shots. These systems support advanced features like optical image stabilization, multiple shooting modes, and enhanced low‑light performance through Night mode and Deep Fusion. In stark contrast, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) retains a single‑lens setup, which, while it delivers excellent day‑to‑day photography results, does not offer the same flexibility as the dual‑camera systems. This limitation means that users who require wide‑angle or telephoto capabilities might find the SE less capable in varied shooting conditions. - The iPhone 16e’s leap in camera technology:
The iPhone 16e represents a significant upgrade in camera technology for Apple’s budget line. It introduces a 48‑megapixel fusion camera that uses a sophisticated pixel‑binning process to deliver both high‑resolution and improved low‑light images. Additionally, the 16e offers dual‑camera versatility by including a 12‑megapixel 2× telephoto lens alongside the main sensor. This dual‑lens system not only expands the range of photographic possibilities—allowing for optical zoom and better portrait shots—but also incorporates advanced features such as a new Smart HDR 5 that further refines image processing in challenging lighting conditions. - Night Mode, Smart HDR, Deep Fusion, and additional shooting modes:
A key differentiator between the older models and the iPhone 16e is the enhancement in camera processing capabilities. Both the iPhone 13 and 14 employ Smart HDR 4 and Deep Fusion to optimize photos in various lighting scenarios, but the iPhone 16e takes it further with Smart HDR 5, offering finer adjustments and more natural results. The addition of advanced night photography features and support for higher resolution image capture (offering options for 24MP and 48MP photos) sets the 16e apart for users who demand exceptional photo quality in both low and high‑light environments. Moreover, the inclusion of a dedicated telephoto option on the 16e broadens its utility, making it a formidable contender even in photography-focused scenarios.
Battery life & charging options
- Battery capacity and performance:
When comparing battery performance across the models, the differences are notable in terms of both capacity and real‑world usage. The iPhone 13 and iPhone 14 models offer battery life that supports around 19–20 hours of video playback, making them sufficient for daily use with moderate media consumption. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen), due to its smaller form factor and 4.7‑inch display, provides a slightly lower video playback time—approximately 15 hours—as well as up to 50 hours of audio playback. In contrast, the new iPhone 16e leverages improvements in both the A18 chip’s efficiency and battery capacity to deliver significantly enhanced performance. With an advertised 26 hours of video playback, 21 hours of streaming video, and an impressive 90 hours of audio playback, the 16e positions itself as a compelling option for power users and those who prioritize extended battery endurance. To make the most of this longevity, keeping your device’s storage optimized can help maintain smooth performance over time. - Fast‑charging and wireless charging standards:
All models in our comparison support fast‑charging and wireless charging, but the underlying capabilities differ. The iPhone 13 and 14 models typically support fast‑charging up to 50% in about 30 minutes when paired with a compatible adapter, and they also feature MagSafe wireless charging as well as Qi compatibility. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen) offers similar fast‑charging speeds, albeit on a smaller battery, and supports Qi wireless charging. The iPhone 16e not only maintains these standards but also benefits from refined energy management and an optimized charging circuit. This means that in addition to matching the fast‑charging speeds (50% in 30 minutes with a 20W adapter), the enhanced efficiency translates to more reliable battery life over the course of a day. - Positioning the iPhone 16e’s enhanced battery life:
The 16e’s enhanced battery life is one of its strongest selling points. With improved capacity and more efficient power management courtesy of the A18 chip, the 16e outperforms the older models in continuous usage scenarios. For users who are heavy streamers, gamers, or frequently engaged in multimedia tasks, the extra battery endurance means fewer interruptions for charging. This advantage, coupled with the support for both fast‑charging and wireless charging, makes the 16e a particularly attractive choice in the budget category, especially when compared to the more compact but lower‑capacity iPhone SE (3rd Gen).
Design, build, & ergonomics
- Modern edge‑to‑edge design with Face ID vs. Classic Touch ID:
The iPhone 13, iPhone 14, and iPhone 16e all showcase Apple’s modern edge‑to‑edge design that emphasizes a large, immersive screen paired with Face ID for secure authentication. This design philosophy not only maximizes display area for media consumption but also supports a minimalist aesthetic that many users appreciate for its seamless look and feel. In contrast, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) reverts to a classic design reminiscent of earlier models, complete with a physical home button housing Touch ID. While this design appeals to users who prefer the tactile familiarity and reliability of Touch ID, it does come with a smaller display and a more dated visual style compared to the contemporary, bezel‑minimized look of the other models. - Material differences:
The premium models (iPhone 13, 14, and 16e) are constructed with high‑quality materials such as glass fronts and backs combined with aluminum frames, offering both a sleek appearance and a sense of modern durability. These materials contribute to a refined look and improved wireless charging performance. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen), while still built with quality materials (often mirroring the design cues of the iPhone 8), uses more traditional elements that underscore its budget positioning. This results in a device that may feel solid and familiar but lacks some of the aesthetic and tactile nuances found in the newer models. - Dimensions, weight, and ease of use:
Ergonomics play a crucial role in the daily usability of a smartphone. The larger 6.1‑inch screens of the iPhone 13, 14, and 16e provide an immersive experience and ample space for multitasking, though they can be slightly more challenging for one‑handed operation. The iPhone 16e, despite its modern, edge‑to‑edge design, manages to remain lightweight and well balanced (approximately 167 g) due to efficient engineering. In contrast, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen)’s compact 4.7‑inch form factor and lower weight (around 144 g) make it exceptionally pocket‑friendly and easy to use with one hand. However, this compactness also limits the display area and may not be ideal for users who prefer a more expansive visual interface.

Connectivity & extra features
- 5G and Wi‑Fi 6/6E differences:
Connectivity is a key factor in modern smartphones. All the models under consideration support 5G, ensuring fast and reliable internet access. However, the iPhone 13, 14, and 16e are equipped with advanced Wi‑Fi 6 or even Wi‑Fi 6E capabilities, offering improved speeds, lower latency, and better performance in crowded networks. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen) also supports 5G and Wi‑Fi 6, but given its older design, it may not incorporate some of the newer enhancements found in the later models, which can be important for users in high‑density network environments. - Unique additions on the iPhone 16e:
The iPhone 16e distinguishes itself with several unique connectivity and extra features that set it apart from its predecessors. It has transitioned to a USB‑C connector, in line with evolving industry standards and regulatory requirements—a significant upgrade over the Lightning connector used in older models. Additionally, the 16e introduces Apple Intelligence features, integrating on‑device AI enhancements that improve photography, app interactions, and system performance. It also offers emergency satellite SOS capabilities, providing a critical safety feature for users in remote areas, as well as improved sensor arrays for more precise environmental and user activity data. - Ecosystem and software support considerations:
Apple’s ecosystem and software support remain a decisive factor for many buyers. The iPhone 13, 14, and 16e, with their modern hardware, are guaranteed to receive several years of iOS updates, ensuring ongoing security, feature enhancements, and compatibility with emerging apps. Features such as Face ID, Apple Pay, and integration with other Apple devices (like the Apple Watch and Mac) enhance the overall user experience. Even the iPhone SE (3rd Gen), despite its classic design, benefits from Apple’s long‑term software support. However, its older hardware may eventually limit access to the newest features. The improved security features, seamless ecosystem integration, and enhanced support offered by the 16e make it particularly appealing for users looking to invest in a device that will remain current and secure for a longer period.
Price, value, and trade‑offs
Older flagship models like the iPhone 13 and iPhone 14 entered the market at premium price points reflective of their high‑end features and design. Over time, as newer models are released, these devices have seen price drops and increased availability in refurbished or discount channels. The
Original price points and availability trends
iPhone SE (3rd Gen) was positioned as a budget alternative from the outset, targeting users who value familiarity and compact design over the latest features. These price adjustments have created a market where legacy models are accessible to buyers looking for proven performance at a reduced cost.
Evaluating “bang for the buck” for the iPhone 16e
The new iPhone 16e is designed as a budget‑oriented entry point into Apple’s ecosystem while still offering many modern features. By integrating the latest A18 chip, an advanced dual‑camera system, and improvements in battery life and connectivity (including USB‑C and emergency satellite SOS), the 16e delivers a surprisingly robust package at a more affordable price. This “bang for the buck” factor makes it highly competitive, especially for buyers who want modern performance and a future‑proof device without the premium cost of flagship models. The enhanced battery and processing capabilities further amplify its value proposition compared to both older high‑end models and the budget SE 3.
Trade‑offs: Advanced features vs. familiarity and compactness
Ultimately, the choice between these models comes down to the trade‑offs inherent in each design. The iPhone 16e offers state‑of‑the‑art features such as improved camera capabilities, longer battery life, modern connectivity (USB‑C), and advanced AI integration—all at a budget‑friendly price. However, it may lack the compact, nostalgic design of the iPhone SE (3rd Gen), which appeals to users who value a smaller, more familiar form factor with a physical home button and Touch ID. Similarly, while the iPhone 13 and iPhone 14 provide a premium feel and robust performance, they carry a higher price tag compared to the 16e. Therefore, consumers must balance their need for advanced, future‑proof features against the comfort and value of tried‑and‑true designs, deciding which trade‑offs align best with their usage patterns and lifestyle.

User experience
Let’s dive in.
Impact of screen size and display type on daily use and media consumption
The choice of screen size and display technology has a profound effect on everyday use. Larger 6.1‑inch OLED displays—as seen on the iPhone 13, 14, and 16e—offer immersive viewing experiences ideal for watching high‑definition videos, browsing rich content, and playing games. These displays deliver deep blacks and vibrant colors, enhancing media consumption and overall user satisfaction. In contrast, the 4.7‑inch LCD of the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) caters to those who prefer a compact, pocket‑friendly device. While its smaller size makes it exceptionally easy to handle and carry, the lower resolution and reduced brightness compared to OLED mean that videos, photos, and graphical content may not appear as sharp or engaging.
The importance of camera quality for casual and professional photography
Camera performance is a key factor for many users—whether capturing everyday moments or pursuing professional photography. The multi‑lens systems on the iPhone 13 and 14 provide versatility in framing, low‑light performance, and optical zoom, making them suitable for a wide range of scenarios. These models, with features like Smart HDR and Deep Fusion, deliver reliable image quality for casual snaps and more challenging photography conditions. On the other hand, the iPhone SE (3rd Gen) offers a single‑lens setup that, while producing excellent photos in daylight, lacks the flexibility and advanced features needed for more diverse shooting scenarios. The iPhone 16e, with its 48‑megapixel fusion camera and additional telephoto option, sets a new benchmark in budget‑oriented photography, appealing especially to users who value high‑resolution and versatile imaging capabilities—even if they are not professional photographers.
Battery performance
Battery life is not just a spec—it directly impacts how often users need to recharge and how reliably the device can support intensive daily use. In practical terms, the iPhone 13 and 14 provide solid endurance for most users with standard media consumption and app usage. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen), due to its smaller battery, may require a recharge sooner under heavy usage. In contrast, the iPhone 16e’s enhanced battery capacity, combined with the efficiency of the A18 chip, ensures that users can enjoy longer periods of uninterrupted activity, whether streaming, gaming, or simply using the phone throughout a busy day. This difference is critical for those who rely on their smartphones for continuous, demanding tasks.
Ergonomics
Ergonomics are key in determining a device’s overall user experience. The larger-screen models (iPhone 13, 14, and 16e) offer immersive displays that can sometimes be challenging for one‑handed use, although their sleek, lightweight designs and well‑balanced proportions help mitigate this issue. These models rely on Face ID for security, which, while fast and secure, may not work as seamlessly in every scenario (for example, when wearing masks). The iPhone SE (3rd Gen) features a classic design with a physical home button and Touch ID, which many users still find more reliable for quick authentication and accessibility. For those who value a compact, familiar feel and tactile feedback, the SE’s design continues to be a strong point.
Software
Apple’s commitment to software updates is one of the strongest aspects of its ecosystem. Modern models like the iPhone 13, 14, and 16e benefit from several years of iOS updates, ensuring the latest features, security enhancements, and performance improvements. The iPhone SE (3rd Gen) also enjoys robust update support; however, its older hardware may eventually limit the use of some advanced features. In a long‑term perspective, investing in a device with the latest hardware (such as the 16e) ensures better future‑proofing, keeping the device compatible with emerging technologies and software innovations over a longer period.

Summary of strengths and weaknesses
- iPhone 13 & iPhone 14:
Strengths: Premium OLED displays with immersive visuals, versatile multi‑lens camera systems, robust performance with the A15 Bionic chip (and enhanced variants), and a modern design with Face ID.
Weaknesses: Higher price points compared to budget models, and, as newer models are released, potential price reductions may make them less attractive in terms of value. - iPhone SE (3rd Gen):
Strengths: Compact, nostalgic design with a physical home button and Touch ID, lower cost, and excellent performance for everyday tasks thanks to the A15 chip.
Weaknesses: Smaller, lower‑resolution LCD display, single‑lens camera system lacking advanced photography features, and relatively shorter battery life under intensive use. - iPhone 16e:
Strengths: Cutting‑edge performance with the new A18 chip, significant battery life improvements, advanced dual‑camera system with a 48‑megapixel sensor and telephoto capability, modern design with USB‑C connectivity, and additional features like Apple Intelligence and emergency satellite SOS.
Weaknesses: May sacrifice the compact, familiar form factor appreciated in the SE series, and while it offers premium features at a budget‑oriented price, it might not match the tactile feel of a Touch ID home button for some users.
Recommendations
- For users who prefer older, proven models (iPhone 13, 14, SE 3):
- Buyers who appreciate the refined, familiar design and proven reliability of previous generations may continue to favor the iPhone 13 or iPhone 14. These models are ideal for those who want a premium experience without the steep cost of the very latest device.
- The iPhone SE (3rd Gen) remains an excellent choice for users who value compactness, tactile feedback through Touch ID, and a traditional design—especially if a smaller form factor is a priority.
- For users considering the new budget‑oriented iPhone 16e:
- The iPhone 16e is tailored for buyers who want modern performance, extended battery life, and advanced camera features at a more accessible price.
- It is especially well‑suited for power users, multimedia enthusiasts, and those looking for a future‑proof device that balances cost with the latest technological advancements, including USB‑C connectivity and enhanced AI features.
Featured image credit: Apple