What is the brain of the computer? We cannot say that the computer-human body analogy is the brightest idea in the world, but we have an answer for you.
What is the brain of the computer?
The central processing unit is the brain of the computer, through which all information travels along with commands and instructions. The CPU, a crucial piece of computer hardware, permits the transfer of instructions between the computer’s components.
What is the CPU?
A microprocessor known as the central processing unit serves as the control hub of electronic devices. Many of the computer’s fundamental instructions are generally handled by the CPU. Still, it can also delegate more complicated jobs and programs to particular chips so that these parts can carry out the data instructions.

CPU stands for…
One of the most crucial components of your computer is the central processor unit or CPU. It can be found on the motherboard and is in charge of carrying out each command issued by an app. Almost everything that happens on your computer involves the CPU, including opening apps, loading data, and displaying images.
Other things outside your laptop or desktop computer have a CPU chip. Your phone has one, as does your gaming console and smartwatch. The dashboard screen of every automobile you’ve purchased in the past 10 years likely has a CPU.
CPUs are vital parts of almost any electronic device today.
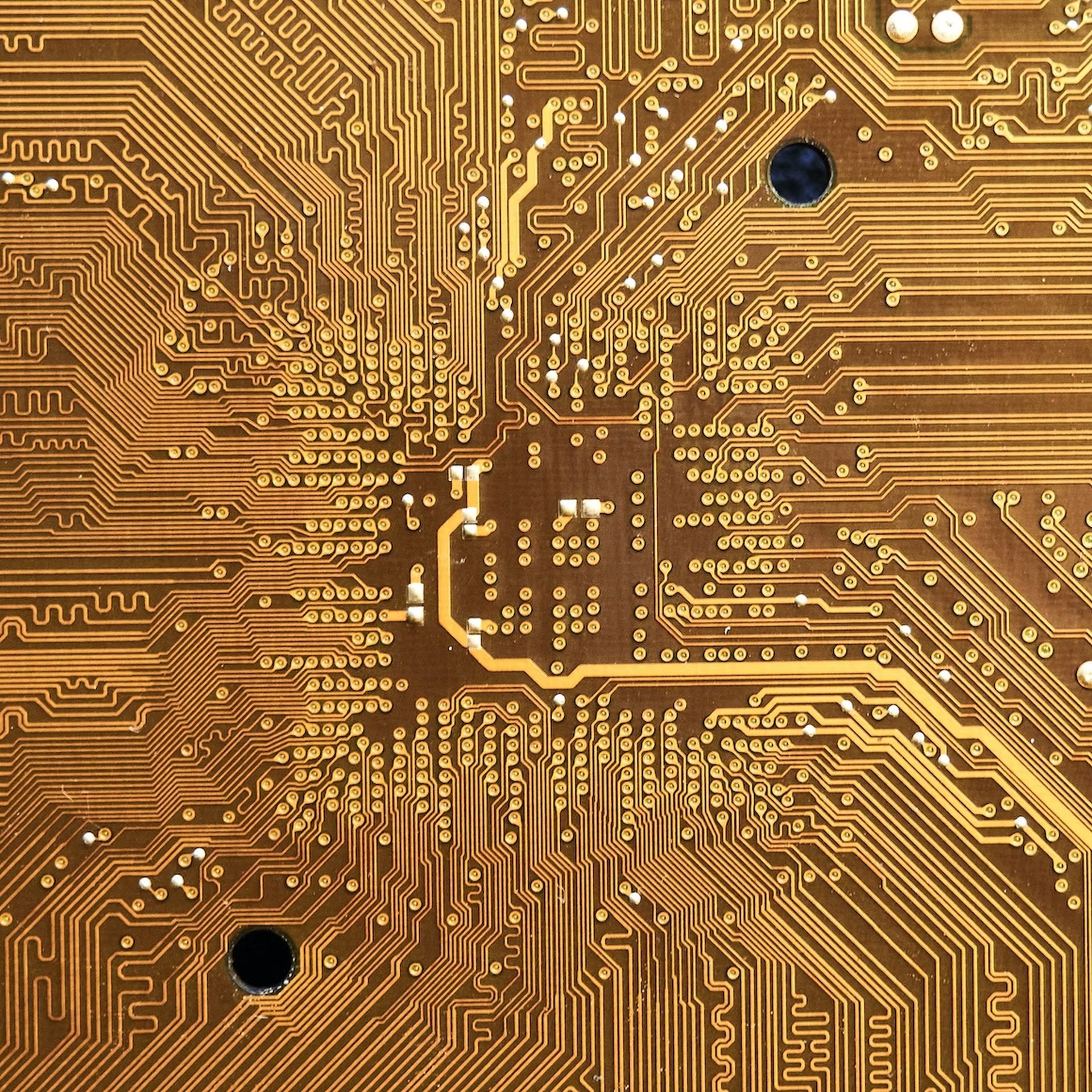
How does the CPU look?
The CPU is an extremely small silicon chip that contains sophisticated integrated circuitry. A single computer chip has billions of tiny transistors. The CPU is powered by transistors, which carry out the instructions needed to operate your computer applications. Transistors are becoming smaller today, which allows your computer’s CPU to operate at higher rates.
For the majority of consumer-focused processing devices, its dimensions are typically between 4mm2 and 10mm2 per core. A CPU features several metallic, rounded connectors on its bottom side. In a CPU, these connectors are taking the place of older-style pins.
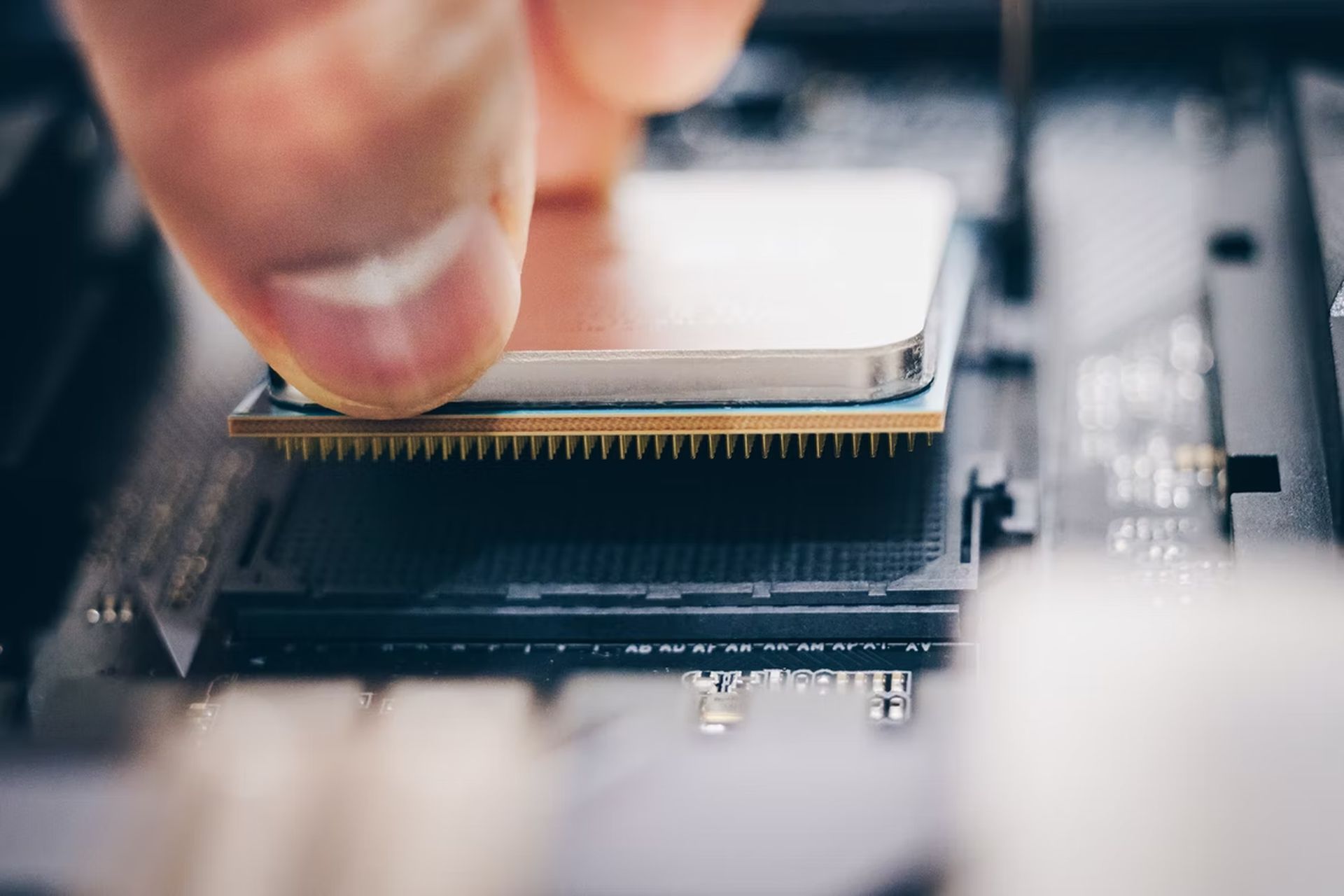
How does a CPU work?
A CPU performs calculations quickly, including processing instructions, adding and subtracting integers, and rearranging data in memory. Your computer’s operation of these commands causes Windows 10 to launch, open a spreadsheet, or play a YouTube video.
Silicon image sensors enable faster image processing
CPUs must process many of the millions of running computer instructions in milliseconds. The ability of a CPU to access instructions from RAM before it needs them is one of its intriguing features. As a result, the CPU can process the instructions more quickly because they have already been pre-logged.

The history of CPUs
In the early 1970s, Intel introduced the first computers with central processing units. The first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, was released by Intel in 1971. The 4004 used more than 2,000 transistors and 640 bytes of memory to accomplish around 60,000 operations per second. Three new Intel microprocessors with 14, 16, and 18 cores each were released in 2017.
The history of data processing technology
Is RAM the brain of the computer?
Some say RAM is the computer’s brain, while others say the operating system is the computer’s brain. But from our perspective, they are wrong.
The hardware in a computing device called “Random Access Memory” (No, we are not talking about your favorite Daft Punk album) stores the operating system (OS), application programs, and data that are currently in use so that the processor of the device can access them rapidly. The primary memory of a computer is RAM.
The CPU is where all the work is done. It processes information using RAM for the incoming data and the final output.
Although the analogy will depend on your definition of brain. The human brain, for instance, processes information and stores memories. Both the permanent storage device (hard drive, SD card, etc.) and the RAM can store data, but neither one can process it.
RAM is a passive data storage device. Most of us associate the word “brain” with the processing carried out by our brains, thus in that sense, the computers attached to the RAM serve as the metaphorical “brain.” But the computer has limited storage capacity. We, therefore, cannot process information without the RAM and the CPU, respectively.
Is the CPU the heart or brain?
The heart in the human body is in charge of maintaining blood pressure and pumping blood throughout the body.
Even while there may be some disagreement about the computer’s heart, comparing it to the northbridge makes the most sense. On the motherboard, there are two chips—the northbridge and the southbridge.
It is in charge of carrying out high-performance tasks like controlling information flow and data routing in computers. It employs buses to transmit data between the CPU and external devices.
The conventional northbridge/southbridge design is no longer present in many systems. Instead, they are merely referred to as a “chipset” and are incorporated into the CPU, enabling faster connection and better functionality.
The CPU will become more functional as computers progress toward a system-on-chip design. As a result, the CPU can be referred to as the brain of the computer.
However, a study conducted in 1979 refers to the CPU as “the heart of any digital computer.”
If you want further information, check out this article called “An Overview of Microprocessor Central Processing Units (CPUs)“
Why CPU is the brain of the computer?
The processor, also known as the CPU, is responsible for the computer’s instructions and processing power. The more competent and up-to-date the processor in your computer, the faster it can do tasks. You may make your computer operate and think more quickly by boosting the CPU.
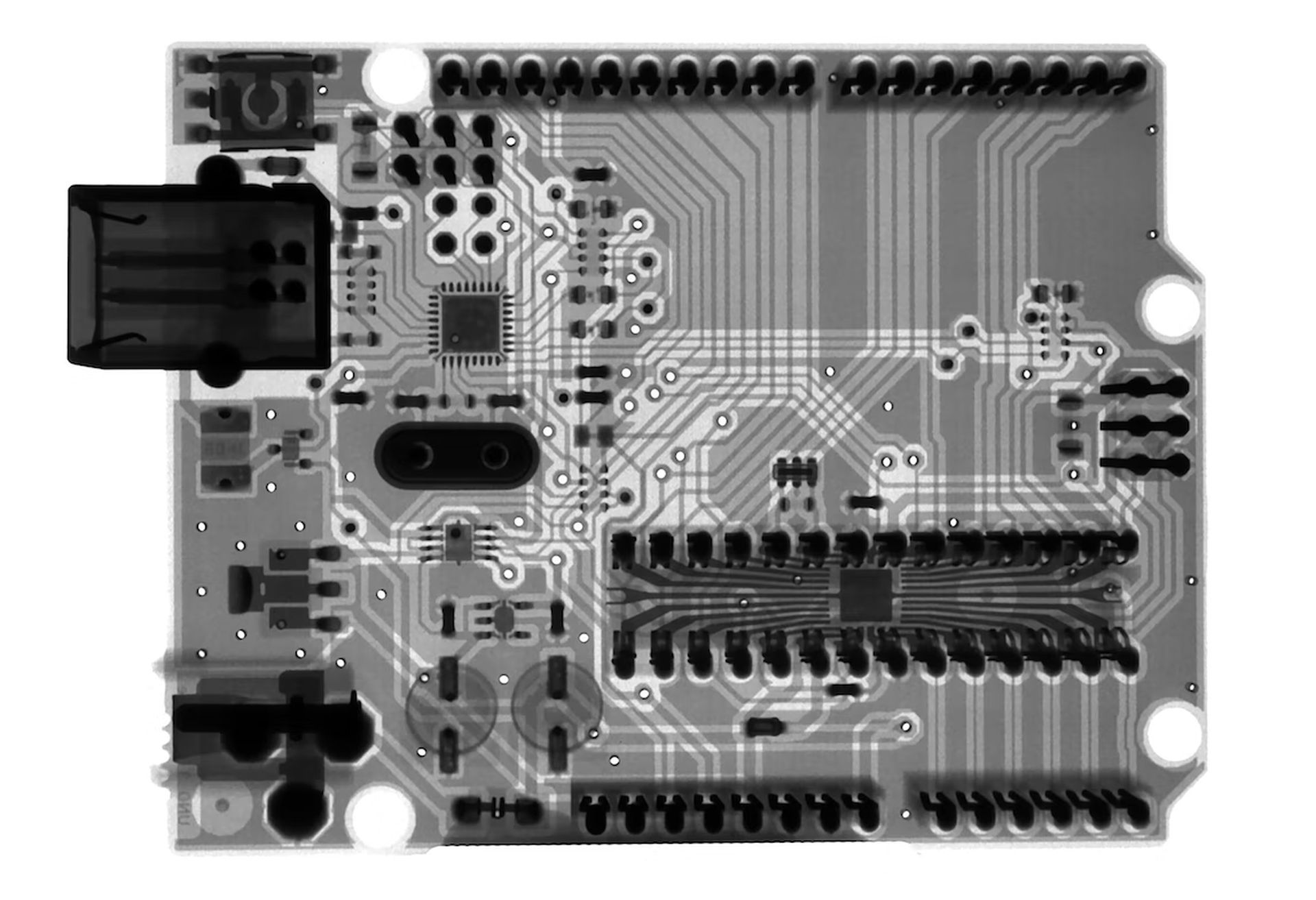
The component of a computer that controls input, stores data, and generates output is known as the central processor unit (CPU). The CPU always complies with software’s requests, which tell it what data to process and how to do so. Without a CPU, programming on a computer is not feasible.
The quantum boost to AI paves the way for AGI
Both use electrical signals to transmit messages. Instead of computers using electricity to transmit information, the brain uses chemicals to do so. Electrical signals can pass across computer cables much more swiftly than they can through the neurological system. Both of them exchange info.
The brain has similar functions to the human body, so when someone asks you a question like “What is the brain of the computer?” you can easily say the CPU is the brain of the computer.
What are two types of memory?
You asked us “What is the brain of the computer?” and we said it could be the CPU. However, to get a deeper understanding, the best thing is to comprehend the different types of memory. The computer’s memory is a crucial component. A computer’s ability to retain, evaluate, and respond appropriately to user commands is a fundamental requirement.
The storing component of a computer’s operation is called memory. The memory also stores data for immediate use and for the hardware components of computers and how they work. The memory performs operations at a high rate to process information in the computer. The numerous types of memory storage available on computers are similar to those in the human brain.

Types of memory in a computer
A computer’s memory can be divided into two categories: primary memory and secondary memory. RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read-only memory) are the main components of the primary memory. The hardware storage components that are independently included, such as HDD (Hard Disk Drives), SSD (Solid State Drives), Compact Disk, and other components, are called secondary memory.
With the support of various memory types, the computer system functions properly. Each form of memory has different advantages and disadvantages, and they are all being improved for the benefit of computer users throughout the globe.
Researches conducted in the area of computer memory to improve the user experience and store the most data has led to major advancements in computer technology. Some computer memory can continue to save information even when there is no electricity.
Analog deep learning paves the way for energy-efficient and faster computing
They are known as non-volatile. Some are referred to as volatile since they can only be stored for a brief time when powered on. The computer’s configuration produces outstanding results if a very good combination of both types of memory is applied. Let’s review the two types of memory below.

Primary memory
Both RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM are included in this type of memory (Read-Only Memory). When the computer is in power mode, the primary memory retains extremely small amounts of data and may be accessed very rapidly.
Secondary memory
The secondary memory components of a computer are typically HDDs and SSDs. They are not as pricey as RAM and ROM. Their writing and reading speed is also noticeably slower. It doesn’t require power to maintain the data stored inside because it is a completely independent device. Before being processed further by the CPU, the RAM receives and stores the exchanged and saved data. In addition to being portable and saving data forever, they are also simple to use and carry around.

Memory usage in a computer
One of the fundamental requirements for the CPU’s operation and the proper operation of the computer is computer memory. CPU-based data processing is accelerated by computer memory (Central Processing Unit). The computer needs to store both temporary and permanent data in order to conduct its processes and respond to human requests by interacting with all the physical components that enable the computer to function. Memory is a fundamental component of every computer system that is necessary for efficiency. The faster the RAM, the more quickly the machine will operate.

Conclusion
The truth of the matter is that it is not the easiest thing to answer a question asking “What is the brain of the computer?” It would be fun to make such an analogy on the CPU, which is the main center of the computer where almost all processes are controlled. Thanks to this interesting joke, we learned the functions of CPU and RAM, which are vital parts of computers. We hope you now know more about how a computer’s memory works.





