All artificial intelligent agents are robots, but is it possible to generalize this to vice versa, that are robots artificial intelligence? Robots and artificial intelligence (AI) have made it possible to find creative answers to the problems encountered by humanity and companies of all sizes across industries. Yet many questions still linger: Is AI a subset of robotics? Does AI fall under robotics? What distinguishes the two terms from one another? Let’s find out!
Are robots artificial intelligence?
First, it should be clear that robotics and artificial intelligence are completely different concepts. These two areas are essentially wholly distinct. The Venn diagram below explains it clearly:
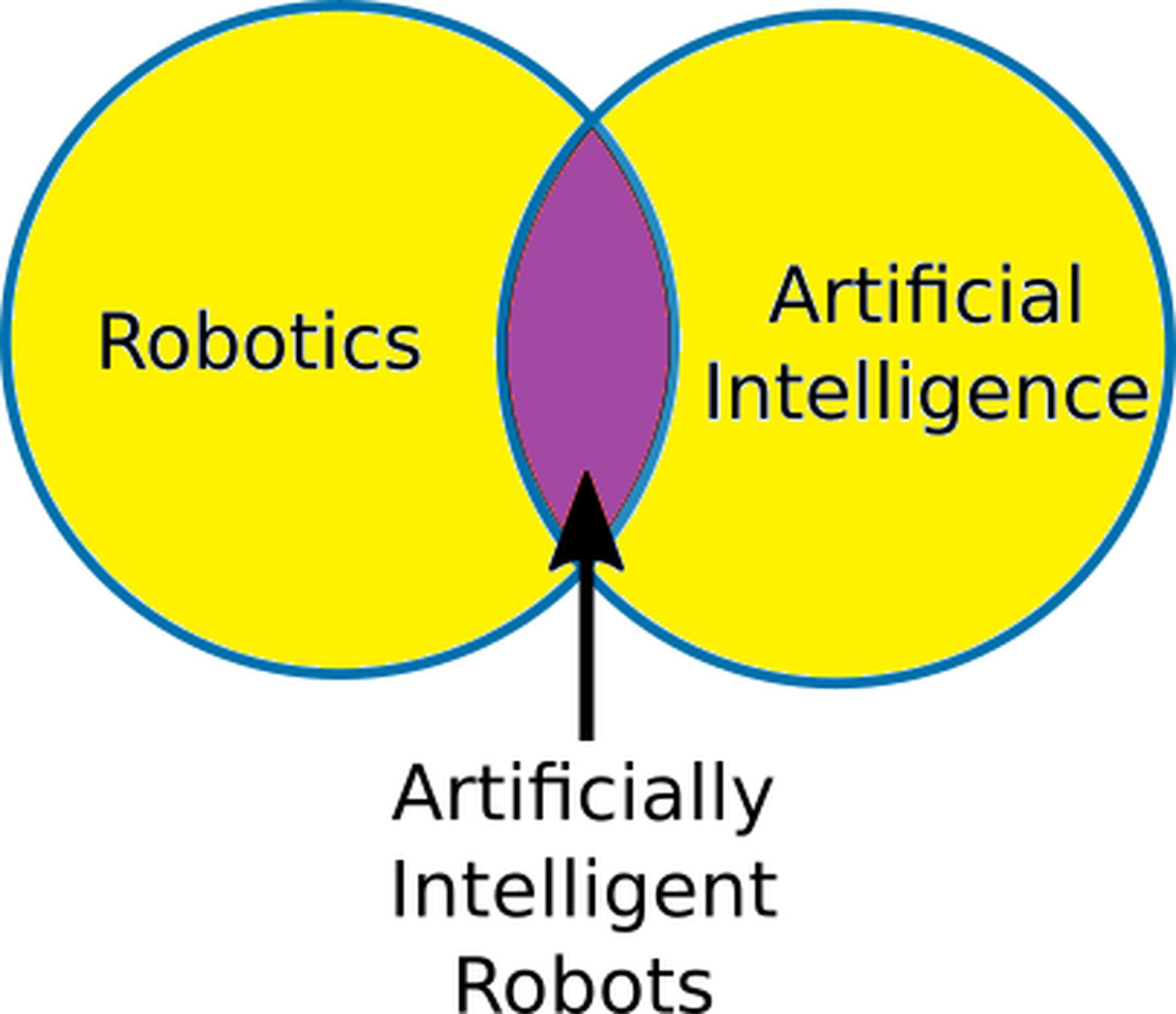
Artificially Intelligent Robots are a small section where the two sciences intersect. People occasionally mix up the two ideas because of this overlap.
We need to examine three concepts separately to answer the “Are robots artificial intelligence?” question.
What is robotics?
Technology that works with robots is called robotics. Robots are programmed machines that often complete a sequence of tasks wholly or partially independently.
Three crucial components make up a robot:
- All robots are made with some form of mechanical design. A robot’s mechanical component aids in its ability to carry out activities in its original setting. For instance, the Mars 2020 Rover’s individual motorized titanium tubing wheels help it maintain a strong hold on the challenging surface of the red planet.

- Electrical parts are necessary for controlling and powering the machinery of robots. Essentially, most robots require an electric current to function (a battery, for instance).
- Robots are at least somewhat computer programmed. A robot would be another piece of basic machinery if it didn’t have a set of instructions directing it on what to do. A robot can know when and how to do a task by programming it.
Engineering’s field of robotics deals with the creation, design, production, and use of robots. Robotics aims to develop smart machines that can help people in various ways.
There are many different types of robotics. A robot could be a machine that looks like a person, or a robotic application like robotic process automation (RPA), mimics how people interact with software to carry out routine, rule-based tasks.
What is artificial intelligence?
The replication of human intelligence functions by machines, particularly computer systems, is known as artificial intelligence. Expert systems, natural language processing, speech recognition, and machine vision are some examples of specific AI applications.
Vendors have been rushing to showcase how their goods and services use AI as the hype surrounding AI has grown. Frequently, what they mean by AI is just one element of AI, like machine learning or robotics. For machine learning algorithms to be effective, they require a foundation of specialized hardware and software. No one programming language is exclusively associated with AI, but a handful are, including Python, R, and Java. We have already explained what programming language for artificial intelligence is the best.
Don’t be scared of AI jargon; we have created a detailed AI glossary for the most commonly used artificial intelligence terms and explain the basics of artificial intelligence as well as the risks and benefits of artificial intelligence.
Use of artificial intelligence in robotics: What are AI-powered robots?
A wide range of sensors are added to AI-powered robots, including vision devices like 2D/3D cameras, vibration sensors, proximity sensors, accelerometers, and other environmental sensors, to provide them with sensing information they can process and act upon in real-time.

Do you know the AI Marl method improves cooperation of robots?
When combined with AI, robots can assist organizations in innovating and transforming their operations. The most prevalent categories of AI-powered robots in use today include:
Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
As they navigate their surroundings, AI gives AMRs the following abilities:
- Information can be captured using 3D cameras and LiDAR sensors.
- Analyze the facts acquired and conclude their environment and overall objective.
- Adapt your behavior to achieve the greatest results.
The activities and tasks carried out by AI-enabled AMRs differ significantly depending on the industry. AMRs, for instance, can avoid collisions by driving around people or fallen boxes when transporting products from one location to another in a warehouse while also figuring out the best route to take.
Articulated Robots (Robotic Arms)
Robots with movable arms can complete jobs more quickly and precisely thanks to AI. AI systems use information from vision sensors, such as 2D and 3D cameras, to divide and comprehend scenes and identify and categorize objects.
Cobots
Cobots can understand and adapt to human speech and gestures thanks to AI, which eliminates the need for worker-assisted training.
Did precursors of artificial intelligence dream of it?
Difference between robotics and artificial intelligence
Although the phrases artificial intelligence and robotics are sometimes used synonymously, they have diverse functions. Since each author and expert has their own interpretation of these terms, there is no unified textbook definition for them, which is the main cause of the misunderstanding.
The question of “Are robots artificial intelligence?” is further deepened by the constant depiction of artificial intelligence and machine learning in popular media as scary robots like the Terminator.
| Robots | AI |
| Robots are machines designed to automatically carry out one or more difficult tasks with the highest accuracy and speed. | AI is similar to a computer program that frequently exhibits some human intelligence traits. |
| Robotics is an area of AI that uses AI to enhance its capabilities. | AI serves as a link between machine learning and human intellect. |
| Robots are autonomous or semi-autonomous machines that process information and use computer systems to control them. | AI is human intelligence that supports human thought to increase task performance and self-improvement. |
| Robots are used for assembly, packaging, earth and space exploration, surgical uses, laboratory research, armament, and other purposes. | Spotify, Apple’s Siri, Netflix, Google DeepMind, and games like Tic-Tac-Toe are among the applications that incorporate AI. |
Now, let’s dive deeper into the difference between robotics and artificial intelligence.
Terminology
Most people mistakenly believe that robots and artificial intelligence (AI) are interchangeable, even though they are two distinct concepts with distinct applications. AI is software, while robots are hardware.
Technically speaking, robots are devices built to carry out one or more simple to complex tasks automatically with the utmost speed and accuracy, whereas AI is similar to a computer program that typically exhibits some of the behaviors connected to human intelligence, such as learning, planning, reasoning, knowledge sharing, problem-solving, and more. The study of intelligent machines that function and respond much like people is known as artificial intelligence (AI).
Technology
The most advanced robotics technology, AI, makes it possible for humans and machines to collaborate in creative ways. In fact, AI systems are made to be substantially different from traditional machine capabilities to appear everywhere we look. In many aspects, artificial intelligence (AI) is human intelligence that supports human intellect to improve task performance.
Robots are intelligent robots that can work autonomously or semi-autonomously. They use artificial intelligence to improve their autonomy through self-learning. They simply use computer systems for information processing and control, simulating human behavior without requiring human involvement.
Applications
Robots are utilized in various fields, particularly in manufacturing and industrial applications. Modern robots are more effective and don’t need specialized software. Additionally, robots are frequently utilized in scientific research, armament, space and earth exploration, surgical applications, assembly, and packing.
Along with robotics, a branch of artificial intelligence, AI is also used in speech recognition. There are other AI consumer applications, such as Apple’s Siri and DeepMind from Google. Also, there are artificial intelligence games that people already play every day.
Are you wonder affect of artificial intelligence in everyday life?
AI in robotics examples
Are robots artificial intelligence? No, but robots can become intelligent, largely thanks to AI.
Robots controlled by AI that can learn from their surroundings and past experiences and then expand on their capabilities based on that knowledge are the most advanced. Let’s look at some of the best examples of AI in robotics.
Starship Delivery Robots
Robotic delivery is a trendy trend, and Starship Technologies delivery robots are among the most well-liked ones.
Starship robots can carry objects up to four miles (six kilometers) away, navigate streets independently, and deliver packages to customers and businesses.
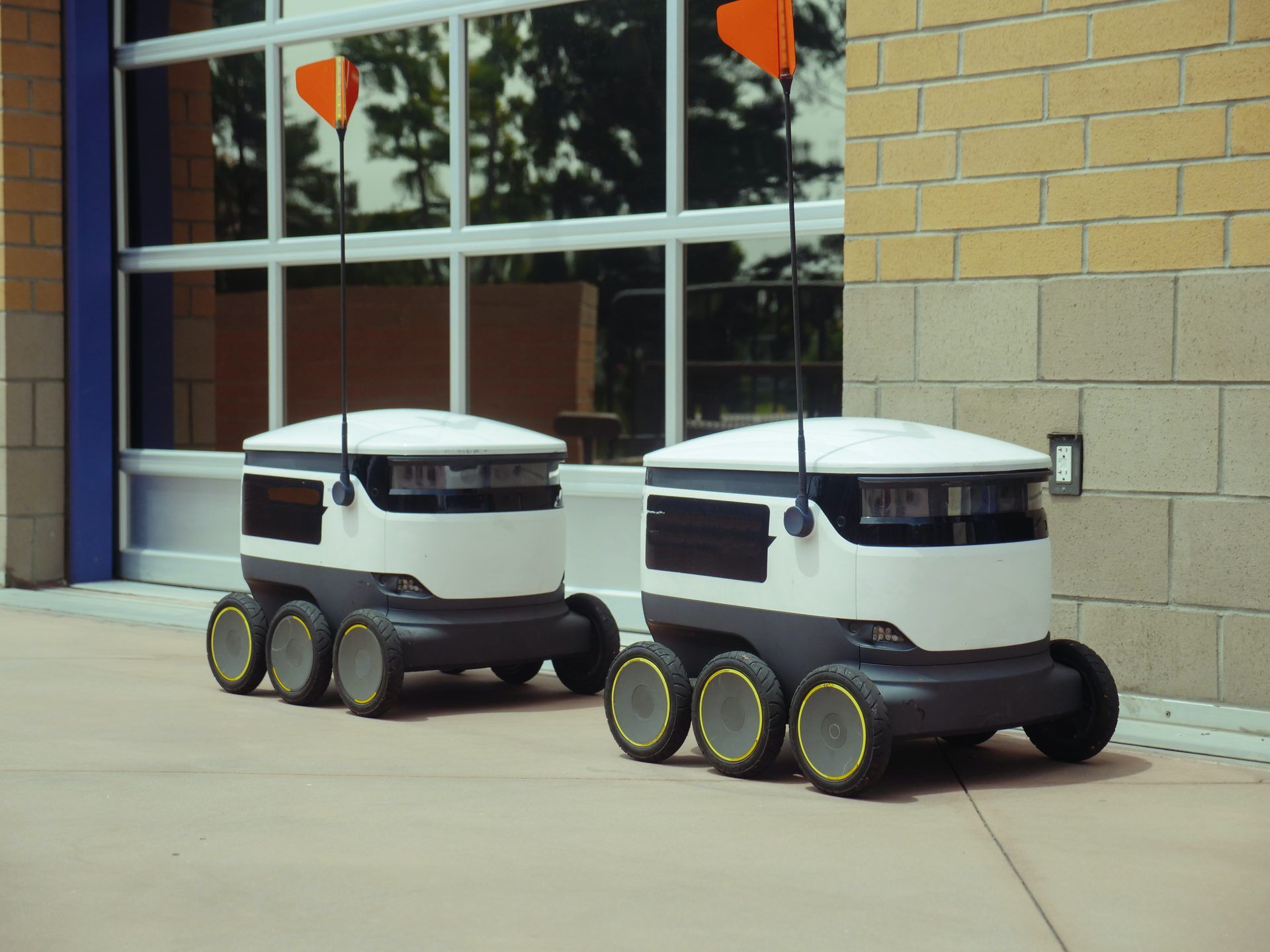

The robots have sensors, artificial intelligence, and a mapping system to help them comprehend their surroundings and whereabouts. They weigh little more than 100 pounds and move at a leisurely pace.
The robots speed up and reduce the cost of local deliveries through collaborations with numerous shops and eateries.
Customers can request the direct delivery of packages and food through a smartphone app. Once requested, a smartphone can be used to track the robots’ whereabouts and routes. It is one of the reasons for the question of “Are robots artificial intelligence?”
Pepper Humanoid Robot
A humanoid robot named Pepper was created to assist people, communicate information with them, and aid shoppers in retail establishments.
Pepper stands around four feet tall, has a tablet in the middle of its breast that displays information, can gesture, and speaks multiple languages.
The robot interprets and reacts to human activities using AI for emotion recognition. It can identify human emotions like joy and respond appropriately, for instance, by smiling.
Pepper can provide tailored suggestions in a shop and direct clients toward the goods they’re looking for. Additionally, it may interact with the human team and sell, cross-sell, and communicate.
Pepper works in places like hospitals, hotels, pizzerias, and banks to enhance customer service and assist businesses in reducing costs.
Penny Restaurant Robot
Penny is an artificially intelligent food-service robot that resembles a bowling pin. It can move food and beverages by itself from a restaurant kitchen to tables and bring dirty dishes back for cleaning.
Penny can operate in various food service settings, including dining rooms, pizzerias, sizable event halls, casino gaming floors, restaurants, and cafés.
This autonomous robot is capable of smoothly delivering multiple drinks at once. It can run during night shifts or busy times because of the long-lasting battery (life of 8–12 hours).
Penny is supposed to deliver the plates to the bus stop so that the line will move more quickly.
As a result, the waiters may concentrate more on enhancing the customer experience, attending to diners’ requirements, and asking how the table liked the meal. It is one of the reasons for the question of “Are robots artificial intelligence?”
Nimbo Security Robot
Nimbo is a robot security guard with various security applications and asset protection built on cutting-edge artificial intelligence technology.
The robot scans and patrols predetermined areas, routes, or self-optimized paths while observing nearby activity and human movement.
When a security breach is discovered, Nimbo can alert the region with light, audio, and video warnings. It compiles video evidence and alerts the human guard in real-time.
The human security personnel can decide which areas to patrol. The robot will then go from location to location while continuously scanning the surroundings.
Nimbo works in stores, workplaces, warehouses, schools, etc., and smoothly connects with VMSs (Video Monitoring Systems).
Shadow Dexterous Hand
A humanoid robot hand that resembles a typical male human hand in size and shape is called the Shadow Dexterous Hand. It may move like a conventional human hand.
It can address issues that demand the closest resemblance to the human hand, having 20 degrees of freedom (more than our hands), and is capable of doing so.
Force sensors and ultra-sensitive touch sensors are among the many sensors found on the hand. It is a teleoperation tool that may also be installed on various robot arms to increase robot capabilities.
There are numerous uses for Shadow Dexterous Hand in numerous industries.
It is ideal for product testing, for instance. The hand can detect and keep track of a wide range of sensory data, including force, micro-vibration, and temperature, thanks to its very accurate sensing skills.
The hand can conduct more dexterous, complicated labor in manufacturing and is accurate and efficient in grasping, lifting, and moving goods.
The robot hand in the agritech industry can assist with tasks like plucking soft produce (like strawberries). Additionally, it can carry out sophisticated tasks in settings that would not be safe for people in the pharmaceutical sector.
Moley Robotic Kitchen System
The world’s first robotic kitchen, a fully automated and intelligent cooking robot system, was developed by Moley Robotics.

A complete set of appliances, cabinetry, computing, security features, and robotic arms are all included in the robotic kitchen system. Using pre-set recipes from the best chefs in the world, it prepares meals with the master chef’s expertise.
The system can accurately imitate the activities of a professional chef, make delectable dishes, and clean up after itself, thanks to a pair of fully articulated robotic hands that mimic human hand movements.
Additionally, it can study recipes, prepare dishes from around the globe, or even prepare your own dishes by yourself.
The robot kitchen can be operated on-site with a touch screen or remotely with a smartphone. The robotic arms retract when not in use to conceal them.
Major airlines, kitchen developers, restaurant sector companies, and even chef training institutes employ Moley.
Flippy Robotic Kitchen Assistant
Flippy is a self-sufficient robotic kitchen assistant who can help cooks make freshly cooked hamburgers and fried meals like tater tots and crispy chicken tenders.
Flippy operates the fryer and the grill. For instance, it can automatically recognize when raw hamburger patties are inserted, keep track of each one in real-time, and switch between spatulas for raw and cooked meat while cooking on the grill.
It can pick up baskets and put them in the fryer, gently shake them while frying the food, watch the cooking time, and other things when cooking.
Flippy’s artificial intelligence brain, which is cloud-connected, allows it to learn from its surroundings and develop new talents over time.
Nomagic Pick-And-Place Robot
The Nomagic pick-and-place robot can take anything out of a box, scan it, and then put it in another box or sorting system.
The robot has the ability to autonomously recognize and choose an object from an unstructured collection of things before putting it into a different box.
One of the monotonous duties still done by people in warehouses is picking and putting items. Additionally, the Nomadic robot automates this process and can complete hundreds of cycles each hour, per day.
The robot’s artificial intelligence allows it to inspect and process each object while analyzing its position, shape, and attributes.
The robot uses barcodes, RFID, or images of the item to identify it. Additionally, to identify any anomalies or quality problems, the inspection task evaluates shape, weight, and motion.
To achieve complete warehouse operations efficiency, the Nomagic robot interacts with your warehouse management system (WMS), warehouse control system (WCS), or proprietary control software. It is one of the reasons for the question of “Are robots artificial intelligence?”
Construction Site Monitoring Robots By Scaled Robotics
The amazing Site Monitoring Robot by Scaled Robotics watches the development of a construction project.
This autonomous robot, which is AI-powered, can roam about building sites, carry out precise scans of ongoing projects, then examine the data to identify faults with quality and track overall progress.
The robot uploads the data it has gathered to the cloud platform for processing. On a unique, color-coded 3D model, users can examine the problems.
This approach assists you in avoiding expensive mistakes and even highlights health or safety issues, such as gaps in edge protection.
Such data must be gathered from many locations on a construction site, which takes time. This artificially intelligent robot ensures that the building is of a high standard while also saving time and reducing waste and rework.
Promobot
Promobot is a business-oriented robot that uses artificial intelligence to move autonomously and interact with humans.
It has the ability to respond to queries, identify faces, provide details about the company’s services, scan, and complete papers, take payments, and display promotional material.
Promobot links to other systems and third-party services, including databases, websites, and online services.
The robot can be used for various tasks as a consultant, promoter, building manager, tour guide, navigation assistant, and assessor who measures health indicators like lung capacity, temperature, and blood sugar.
AI robotics companies
Even though robot technology driven by artificial intelligence (AI) is frequently vilified in sci-fi movie situations, several inventors have demonstrated how using such technology for robotics can promote innovation.

Here are some of them:
Diligent Robotics
AI company Diligent Robotics is developing robot assistants to aid healthcare professionals with everyday chores. The first robot colleague from the business, Moxi, assists clinical personnel in hospitals with non-patient-facing chores so they may spend more time caring for patients.
The Moxi robot can distribute PPE, deliver medication, deliver lab samples, retrieve items from the central supply, and run patient supplies. Moxi’s robotic arm allows it to affect its surroundings, such as opening doors and elevators, and AI technology allows it to learn what to do in a new facility swiftly.
Boston Dynamics
Boston Dynamics creates sensor-based controls that equip robots for various situations and terrains to produce dynamic, intelligent, and adaptable robots. The Netflix Black Mirror episode Metalhead was inspired by the company’s SpotMini miniature robot.
Atlas, a dynamic humanoid robot developed by Boston Dynamics, has completed a parkour course and has hardware that allows it to exhibit agility comparable to that of a human. Spot, Stretch, and Pick are automated solutions that help warehouse operations and are a new addition to its family of robots.
Miso Robotics
Miso Robotics develops AI robotic products for restaurants that can be utilized in industrial kitchens. The company’s kitchen robot, Flippy, has thermal and 3D vision, allowing it to learn from its environment and pick up new abilities. This AI-powered robotic kitchen assistant offers a complete frying solution made to improve restaurant kitchen efficiency.
Miso Robotics’ Flippy can counter increased labor expenses by automating the activity at the frying station.
Conclusion
The fascinating area of robotics is undoubtedly artificial intelligence (AI). Everyone believes a robot can function in an assembly line, but there is disagreement about whether a robot will ever be human-like in intelligence.

You can see that robotics and artificial intelligence are actually two distinct concepts. Robotics entails creating robots, but AI entails creating intelligence.
The AI’s capacity for decision-making sets it apart from other systems. It could improve the software’s output, i.e. improvisation. AI is a wired, programmed technological brain. Robots cannot operate alone or somewhat autonomously without prior instructions or codes of instruction.





