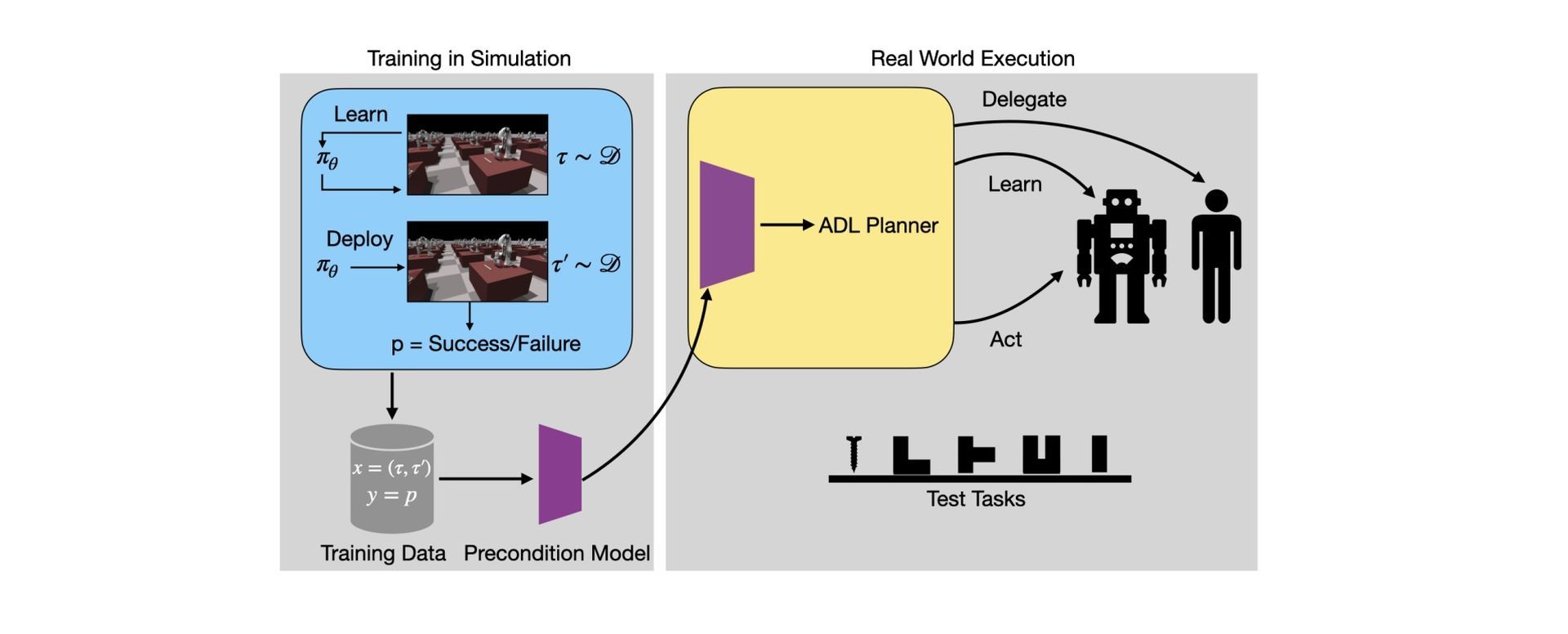
An algorithmic planner developed by a team at Carnegie Mellon University’s Robotics Institute (RI) can aid in delegating tasks to humans and robots. The planner, named “Act, Delegate, or Learn,” considers a list of activities before determining the best method to distribute them.
The algorithmic planner can aid in delegating tasks to humans and robots
The paper is titled “Synergistic Scheduling of Learning and Allocation of Tasks in Human-Robot Teams,” It was presented at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Philadelphia. The researchers are focused on three main questions in the study:
- When should a robot act to complete a task?
- When should a task be delegated to a human?
- When should a robot learn a new task?
“There are costs associated with the decisions made, such as the time it takes a human to complete a task or teach a robot to complete a task and the cost of a robot failing at a task. Given all those costs, our system will give you the optimal division of labor,” said Shivam Vats, the lead author and a Ph.D. student in the RI.
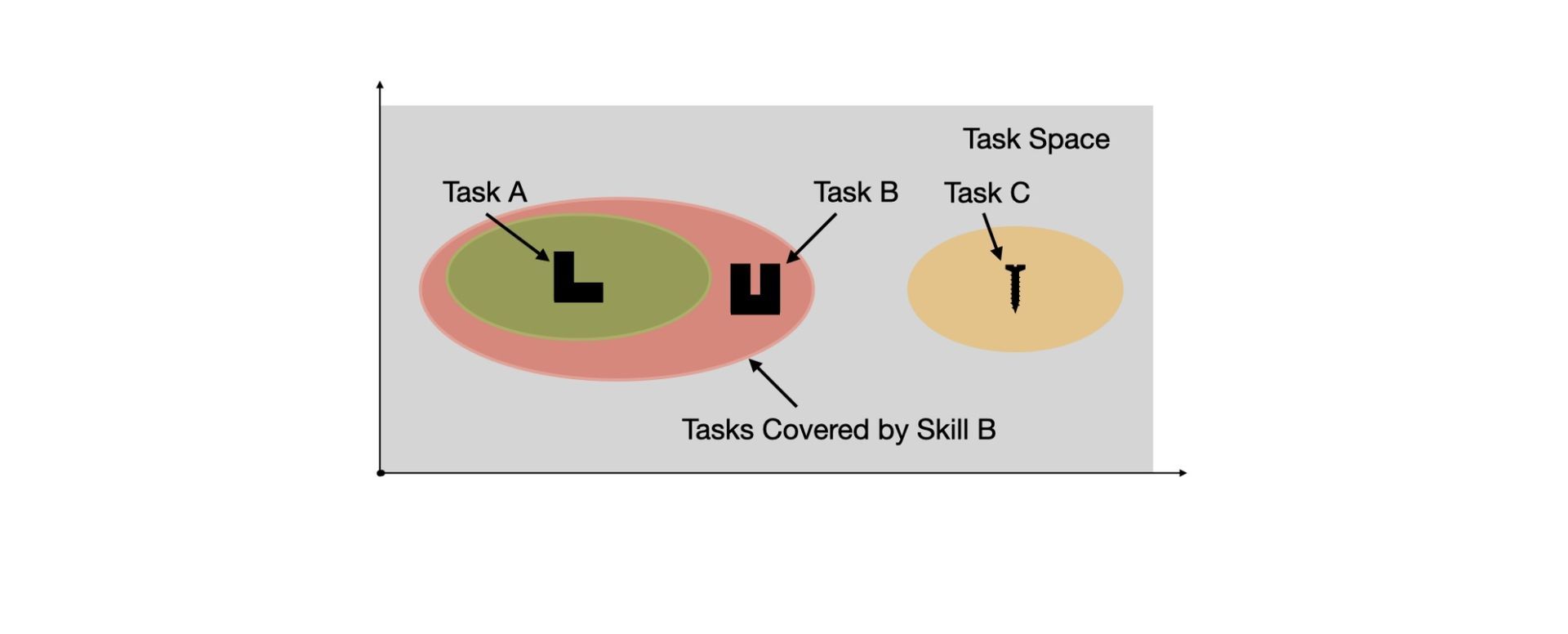
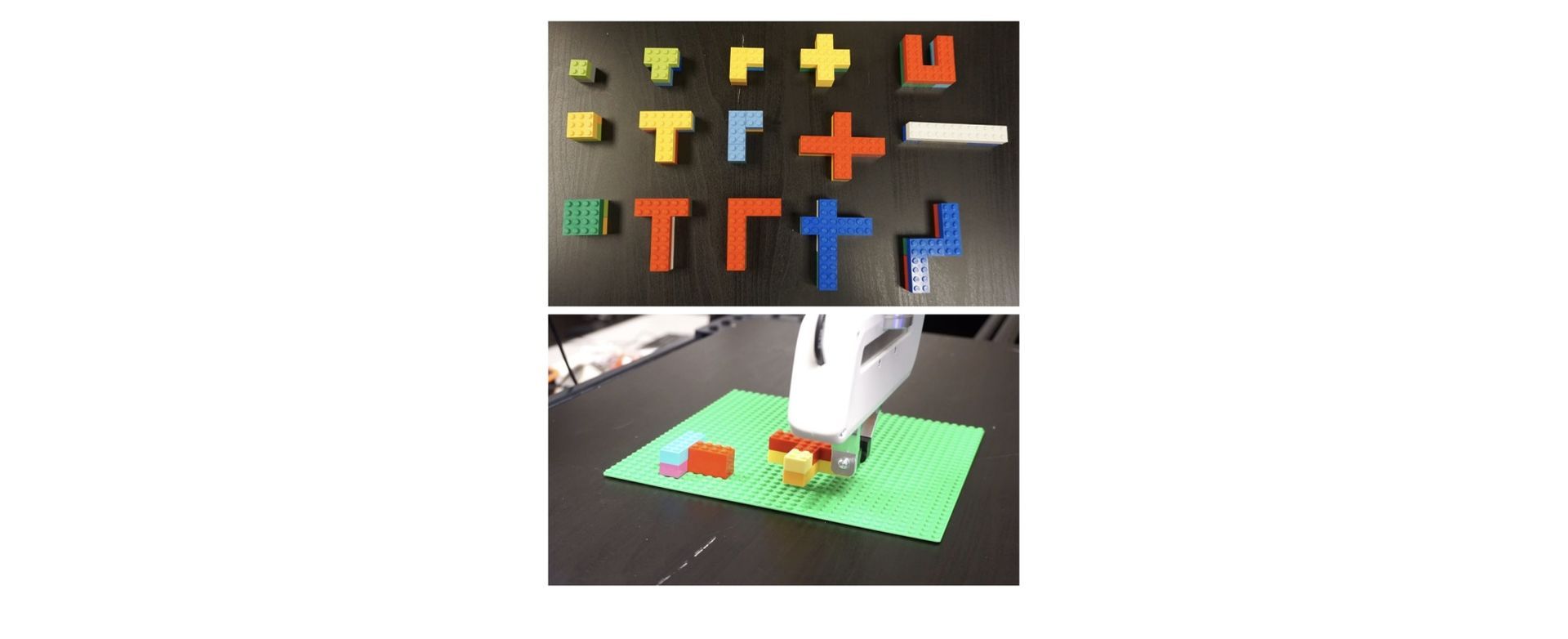
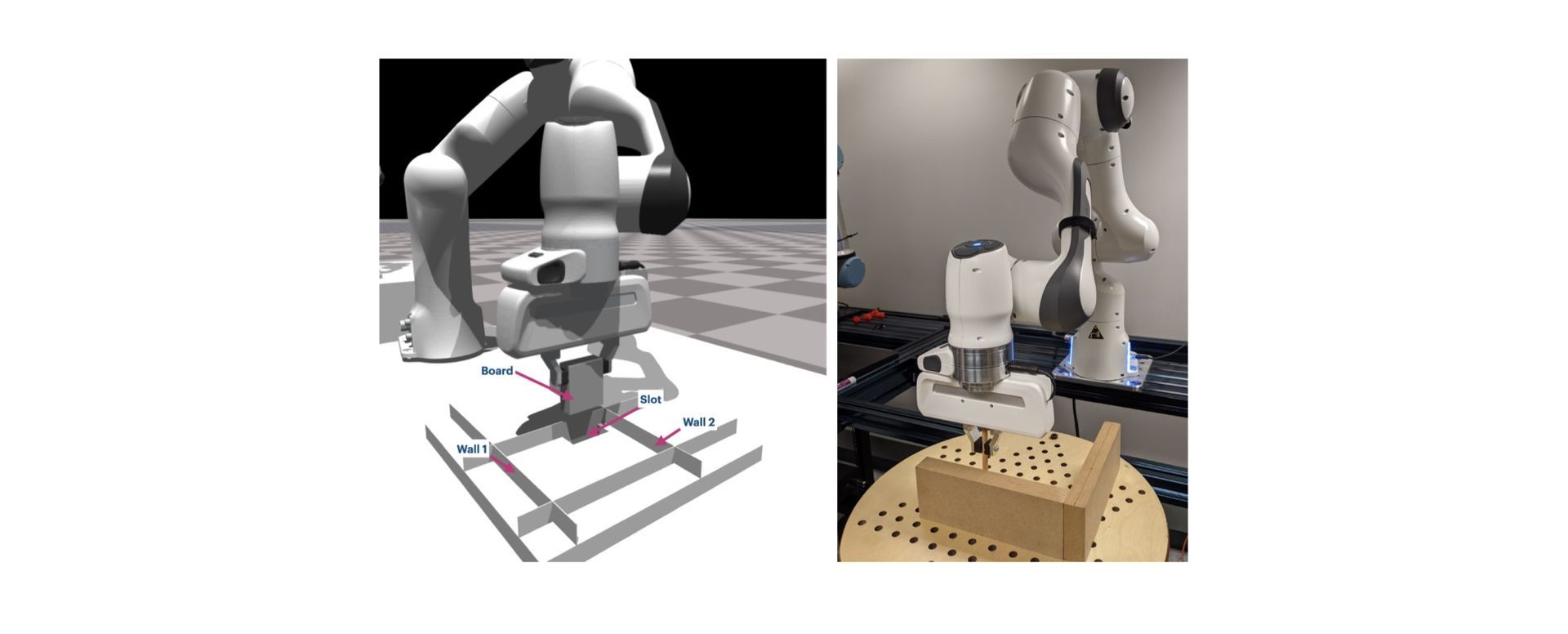
The work may be useful in manufacturing and assembly facilities and other settings where humans and robots collaborate to finish numerous duties. Using a model where people and machines put blocks into a peg board and stack parts of various forms and sizes manufactured of Lego bricks, the algorithmic planner was tested, as can be seen below.

“This planning problem results in a search tree that grows exponentially with n – making standard graph search algorithms intractable. We address this by converting the problem into a mixed-integer program that can be solved efficiently using off-the-shelf solvers with bounds on solution quality. To predict the benefit of learning, we use an approximate simulation model of the tasks to train a precondition model parameterized by the training task. Finally, we evaluate our approach on peg insertion and Lego stacking tasks- both in simulation and real-world, showing substantial savings in human effort,” explained the authors.
Delegating and dividing labor, even when robots are on the team, is not new. But this study is also one of the first to include robot learning in its reasoning.
“Robots aren’t static anymore. They can be improved, and they can be taught,” said Vats.
In manufacturing, a human may manually operate a robotic arm to instruct the machine on how to accomplish a procedure. Teaching a robot takes time and, as a result, has an expensive up-front price tag. However, if the robot can learn a new skill and predict what other activities it could execute after learning one, it may be advantageous in the long run. The ability of a robot to anticipate what additional jobs it might do once it learns a new skill is part of its complexity. If you are new to artificial intelligence and machine learning in the industry, check out our article entitled AI in manufacturing: The future of Industry 4.0.
Given this data, the algorithmic planner transforms the issue into a mixed-integer program – an optimization technique frequently used in scheduling, production planning, and network design – that may be efficiently handled by off-the-shelf software. In all cases, the algorithmic planner outperformed traditional models and lowered task completion costs by 10% to 15%. The efficiency that artificial intelligence brings to the table is undeniable. In today’s world, AI drives the Industry 4.0 transformation, and every expert should keep an eye open.
Vats presented his paper “Synchronous Scheduling of Learning and Allocation of Tasks in Human-Robot Teams,” which was nominated for the outstanding interaction paper award at the International Conference on Robotics and Automation in Philadelphia. Maxim Likhachev, an associate professor from RI, and Oliver Kroemer, an assistant professor from RI, were among the study’s authors. The study was conducted with assistance from the Office of Naval Research and the Army Research Laboratory.





